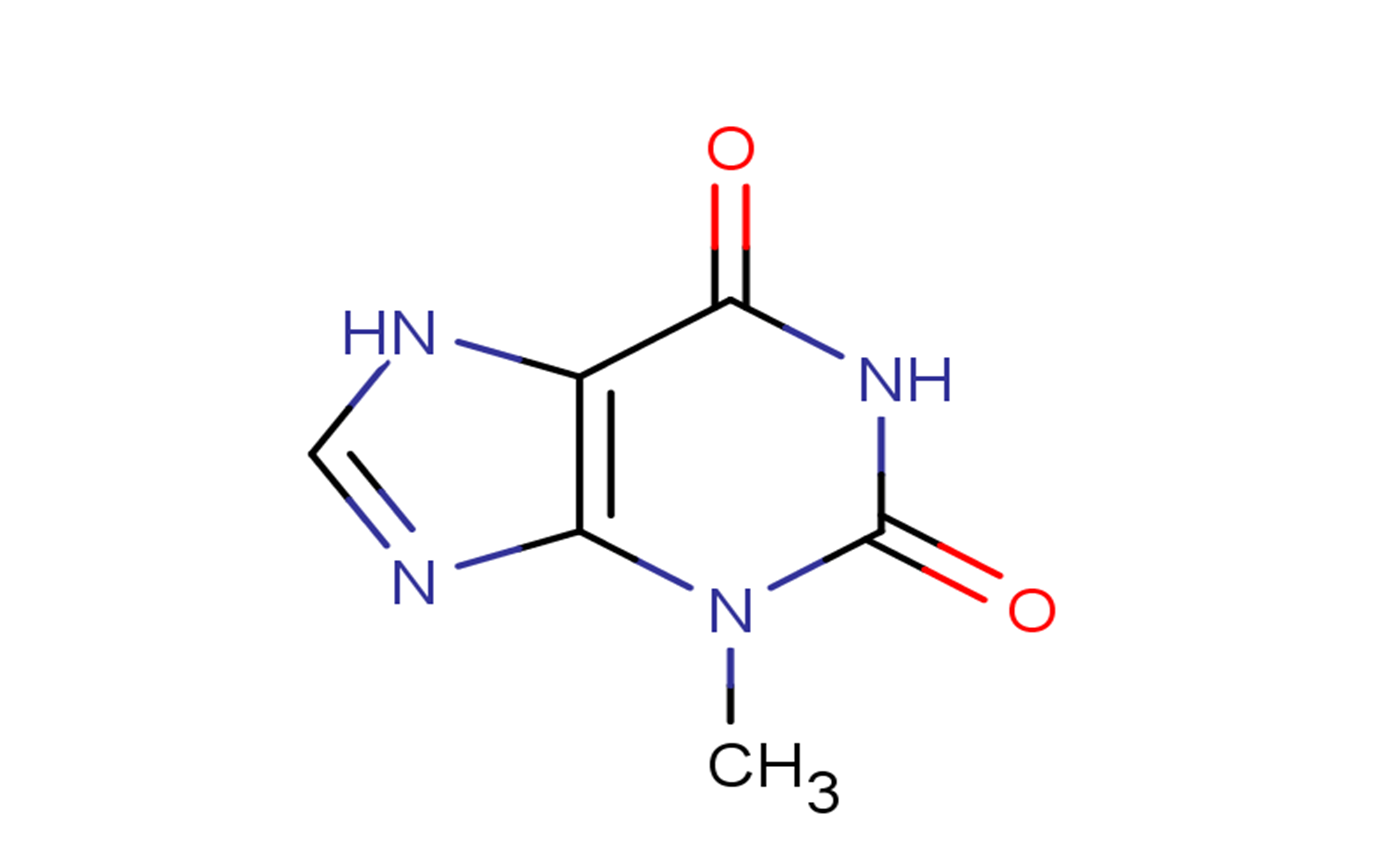
3-Methylxanthine
CAS No. 1076-22-8
3-Methylxanthine( —— )
Catalog No. M23284 CAS No. 1076-22-8
3-Methylxanthine, a xanthine derivative, is a cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP) inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 27 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name3-Methylxanthine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description3-Methylxanthine, a xanthine derivative, is a cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP) inhibitor.
-
Description3-Methylxanthine, a xanthine derivative, is a cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP) inhibitor, with an IC50 of 920 μM on guinea-pig isolated trachealis muscle.3-Methylxanthine inhibited xanthine crystallization, it could protect patients with xanthinuria from the development of renal xanthine calculi.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1076-22-8
-
Formula Weight166.1
-
Molecular FormulaC6H6N4O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:2.61 mg/mL (15.71 mM; Need ultrasonic);1M NaOH:50 mg/mL (300.95 mM; ultrasonic and adjust pH to 11 with 1M NaOH)
-
SMILESCN1C2=C(C(=O)NC1=O)NC=N2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Xanthine urolithiasis: Inhibitors of xanthine crystallization. PLoS One. 2018 Aug 29;13(8):e0198881.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Isobutyric acid
Isobutyric acid is a carboxylic or short chain fatty acid with characteristic sweat-like smell. Small amount of isobutyrate is generated via microbial (gut) metabolism.
-
Pyrrole-2-carboxylic...
Pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid was first identified as a degradation product of sialic acids then as a derivative of the oxidation of the D-hydroxyproline isomers by mammalian D-amino acid oxidase.
-
Isonicotinic acid
Isonicotinic acid is a metabolite of Isoniazid.Isonicotinic acid is a useful isomer of nicotinic acid.?Isoniazid is converted to Isonicotinic acid by hydrazinolysis, with the biotransformation also to be catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as CYP2C.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


