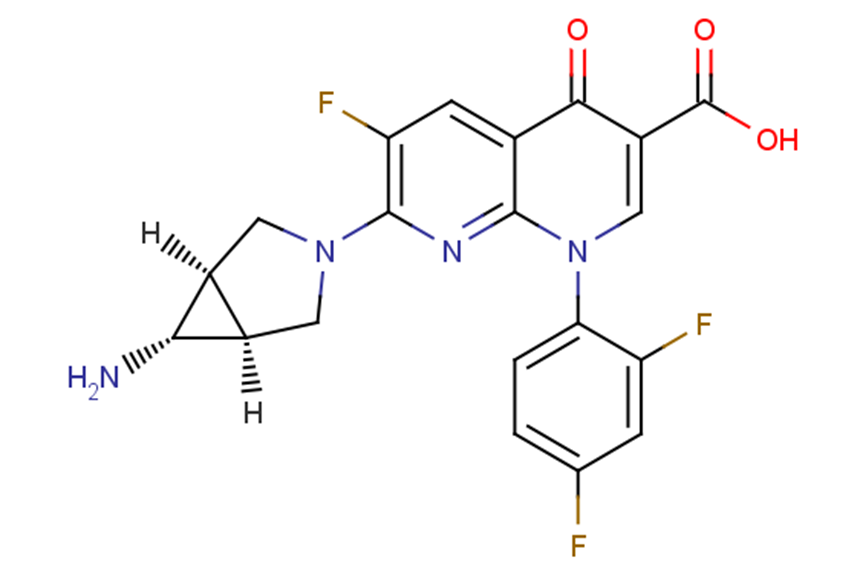
Trovafloxacin
CAS No. 147059-72-1
Trovafloxacin( —— )
Catalog No. M22366 CAS No. 147059-72-1
Trovafloxacin is a broad-spectrum quinolone antibiotic with potent activity against Gram-positive. In HepG2 cells, Trovafloxacin (20 μM; 24 hours; ) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF; 4 ng/mL) incubation induces apoptosis and increases leakage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 67 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 95 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 159 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 232 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 427 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameTrovafloxacin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionTrovafloxacin is a broad-spectrum quinolone antibiotic with potent activity against Gram-positive. In HepG2 cells, Trovafloxacin (20 μM; 24 hours; ) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF; 4 ng/mL) incubation induces apoptosis and increases leakage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).
-
DescriptionTrovafloxacin is a broad-spectrum quinolone antibiotic with potent activity against Gram-positive. In HepG2 cells, Trovafloxacin (20 μM; 24 hours; ) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF; 4 ng/mL) incubation induces apoptosis and increases leakage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Trovafloxacin (20 μM; 24 hours; HepG2 cells) and TNF (4 ng/mL) incubation increases expression of early NF-κB-related factors A20 and IκBα. Trovafloxacin prolongs TNF-induced activation of MAPKs and IKKα/β activation in HepG2. Trovafloxacin is a potent TO-PRO-3 uptake inhibitor by apoptotic cells. Trovafloxacin also inhibits ATP release from apoptotic cells. Trovafloxacin is equally active against both penicillin-susceptible and -resistant pneumococci, with MICs of 0.06-0.25 mg/mL reported for more than 700 isolates. The MICs of Trovafloxacin at which 90% of isolates are inhibited for 55 isolates of pneumococci is 0.125 μg/mL.In male C57BL/6 J mice, TNF-induced p65 nuclear translocation disrupted by Trovafloxacin (150 mg/kg; oral administration). Trovafloxacin treatment increases expression of early NF-κB-related factors A20 and IκBα. Trovafloxacin increased serum levels of alanine amino transferases (ALT) and pro-inflammatory cytokines when administered in combination with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or TNF to mice induces severe liver toxicity associated with vast apoptotic areas in the liver.
-
In VitroTrovafloxacin (20 μM; 24 hours; HepG2 cells) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF; 4 ng/mL) incubation induces apoptosis and increases leakage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in HepG2 cells.Trovafloxacin (20 μM; 24 hours; HepG2 cells) and TNF (4 ng/mL) incubation increases expression of early NF-κB-related factors A20 and IκBα.Trovafloxacin prolongs TNF-induced activation of MAPKs and IKKα/β activation in HepG2.Trovafloxacin is a potent inhibitor of TO-PRO-3 uptake by apoptotic cells. Trovafloxacin also inhibits ATP release from apoptotic cells. Trovafloxacin does not inhibit caspase 3/7 activation, or caspase-mediated PANX1 cleavage during apoptosis.Trovafloxacin is equally active against both penicillin-susceptible and -resistant pneumococci, with MICs of 0.06-0.25 mg/mL reported for more than 700 isolates. The MICs of Trovafloxacin at which 90% of isolates are inhibited for 55 isolates of pneumococci is 0.125 μg/mL.Apoptosis Analysis Cell Line:HepG2 cells Concentration:20 μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Showed a gradual increase of Annexin V-staining and an increased leakage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) at 24 h.RT-PCR Cell Line:HepG2 cells Concentration:20 μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Caused a higher increase in the transcription of A20 and IκBα in HepG2 cells.
-
In VivoTrovafloxacin (150 mg/kg; oral administration; male C57BL/6 J mice) treatment disrupts TNF-induced p65 nuclear translocation. Trovafloxacin treatment increases expression of early NF-κB-related factors A20 and IκBα.Trovafloxacin, when administered in combination with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or TNF to mice induces severe liver toxicity associated with vast apoptotic areas in the liver, increased serum levels of alanine amino transferases (ALT) and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Animal Model:Male C57BL/6 J mice (9-11-week-old) injected with recombinant murine TNF ion Dosage:150 mg/kg Administration:Oral administration Result:Showed a greater number of cells with increased nuclear/cytoplasmic p65 ratio in liver.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetDNA gyrase
-
RecptorDNA gyrase|Topoisomerase|bacterial
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number147059-72-1
-
Formula Weight416.35
-
Molecular FormulaC20H15F3N4O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 10 mg/mL (24.02 mM)
-
SMILESO=C(C1=CN(C2=CC=C(F)C=C2F)C3=NC(N4C[C@@]5([H])[C@H](N)[C@@]5([H])C4)=C(F)C=C3C1=O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Giustarini G, et al. The hepatotoxic fluoroquinolone trovafloxacin disturbs TNF- and LPS-induced p65 nuclear translocation in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 15;391:114915.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Norfloxacin
Norfloxacin(Norxacin) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
-
Balofloxacin
Balofloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic, inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial DNA by interference with the enqyme DNA gyrase.
-
Levofloxacin hydroch...
Levofloxacin is a broad-spectrum, third-generation fluoroquinolone antibiotic and optically active L-isomer of ofloxacin with antibacterial activity. Levofloxacin diffuses through the bacterial cell wall and acts by inhibiting DNA gyrase (bacterial topoisomerase II), an enzyme required for DNA replication, RNA transcription, and repair of bacterial DNA.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


