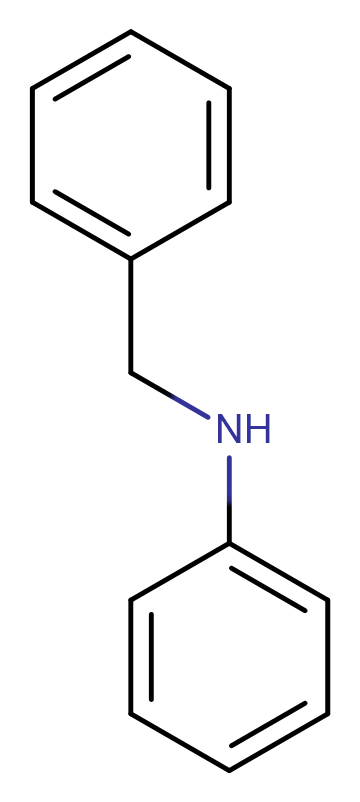
N-Phenylbenzylamine
CAS No. 103-32-2
N-Phenylbenzylamine( —— )
Catalog No. M10161 CAS No. 103-32-2
A series of benzylaniline hydrochlorides as potential cytotoxic and antimitotic agents acting by inhibition of tubulin polymerization.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 34 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 98 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 129 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 181 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameN-Phenylbenzylamine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA series of benzylaniline hydrochlorides as potential cytotoxic and antimitotic agents acting by inhibition of tubulin polymerization.
-
DescriptionA series of benzylaniline hydrochlorides as potential cytotoxic and antimitotic agents acting by inhibition of tubulin polymerization.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCytoskeleton/Cell Adhesion Molecules
-
TargetMicrotubule/Tubulin
-
RecptorTubulin polymerization
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number103-32-2
-
Formula Weight183.25
-
Molecular FormulaC13H13N
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityLimited solubility
-
SMILESC(NC1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Cushman M, et al. J Med Chem. 1993 Sep 17;36(19):2817-2
molnova catalog



related products
-
Vincristine sulfate
Vincristine (sulfate) is an inhibitor of polymerization of microtubules by binding to tubulin with IC50?of 32 μM.
-
DZ-2384
DZ-2384 (DZ2384) is a microtubule-targeting agent, exhibits potent antitumor activity in models of multiple cancer types.
-
SSE15206
SSE15206 is a microtubule polymerization inhibitor that overcomes multidrug resistance. Causes aberrant mitosis resulting in G2/M arrest due to incomplete spindle formation in cancer cells.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


