Verofylline
CAS No. 66172-75-6
Verofylline( —— )
Catalog No. M34733 CAS No. 66172-75-6
Verofylline (Verofyllinum) is an orally available, long-acting, multiacting, methylxanthine-substituted bronchodilator with inhibitory effects on PDE4 for the treatment of asthma disease research obesity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 222 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 333 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 504 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 790 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1086 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1431 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 2871 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameVerofylline
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionVerofylline (Verofyllinum) is an orally available, long-acting, multiacting, methylxanthine-substituted bronchodilator with inhibitory effects on PDE4 for the treatment of asthma disease research obesity.
-
DescriptionVerofylline (Verofyllinum) is an orally available, long-acting, multiacting, methylxanthine-substituted bronchodilator with inhibitory effects on PDE4 for the treatment of asthma disease research obesity.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetPDE
-
RecptorPDE
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number66172-75-6
-
Formula Weight250.3
-
Molecular FormulaC12H18N4O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
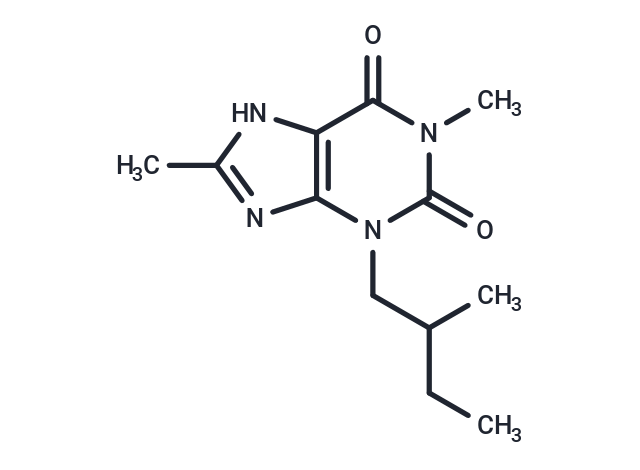
SMILESC(C(CC)C)N1C2=C(C(=O)N(C)C1=O)NC(C)=N2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
HT-0712
HT-0712 (IPL-455903) is a novel potent, selective PDE4 inhibitor with IC50 of 0.15 uM for PDE4D3.
-
Arofylline
Arofylline is a PDE4 inhibitor and can be used for asthma studies.
-
Propentofylline
Propentofylline (Hextol) is a methylxanthine derivative with neuroprotective, antiproliferative, and anti-inflammatory activity and enhanced synaptic adenosine signaling, which may be useful in the study of Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, cognitive impairment, dementia, and chronic pain.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


