RN-1665
CAS No. 1803003-65-7
RN-1665( —— )
Catalog No. M37081 CAS No. 1803003-65-7
RN-1665 is a potent and selective TRPV4 receptor antagonist.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 157 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 216 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 357 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 463 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 637 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 840 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameRN-1665
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionRN-1665 is a potent and selective TRPV4 receptor antagonist.
-
DescriptionRN-1665 is a potent and selective TRPV4 receptor antagonist.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetTRP/TRPV Channel
-
RecptorTRP/TRPV Channel
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1803003-65-7
-
Formula Weight513.54
-
Molecular FormulaC20H24F5N3O3S2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
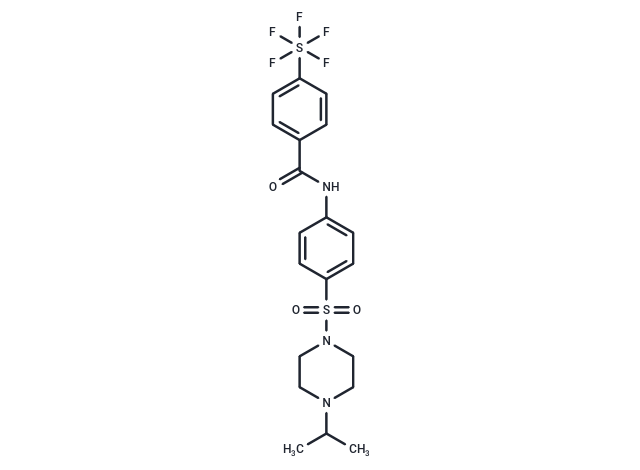
SMILESO=C(NC1=CC=C(S(N2CCN(C(C)C)CC2)(=O)=O)C=C1)C3=CC=C(S(F)(F)(F)(F)F)C=C3
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
(S)-ABT 102
N-[(1S)-5-tert-butyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-yl]-N'-1H-indazol-4-ylurea is a potent TRPV1 antagonist, blocking activation of TRPV1 by capsaicin with the IC50 of 123 nM.
-
ABT 102
ABT 102 is a selective antagonist of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor.
-
TRPC6-PAM-C20
TRPC6-PAM-C20 is a selective TRPC6 positive allosteric modulator. TRPC6-PAM-C20 induces transient increase in intracellular Ca2+ in HEK cells expressing TRPC6 with an EC50 of 2.37 μM. TRPC6-PAM-C20 enhances OAG-induced platelet aggregation.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


