Aptiganel
CAS No. 137159-92-3
Aptiganel( —— )
Catalog No. M34164 CAS No. 137159-92-3
Aptiganel (CNS-1102) is a non-competitive NMDA antagonist, a peptide that may be used to study acute ischemic stroke.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 445 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 686 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 938 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 1398 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1822 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAptiganel
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAptiganel (CNS-1102) is a non-competitive NMDA antagonist, a peptide that may be used to study acute ischemic stroke.
-
DescriptionAptiganel (CNS 1102 (free base)), peptide, is a noncompetitive NMDA antagonist with cerebroprotective effects. Aptiganel can be used for the research of stroke.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetNMDAR
-
RecptorNMDAR
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number137159-92-3
-
Formula Weight303.4
-
Molecular FormulaC20H21N3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
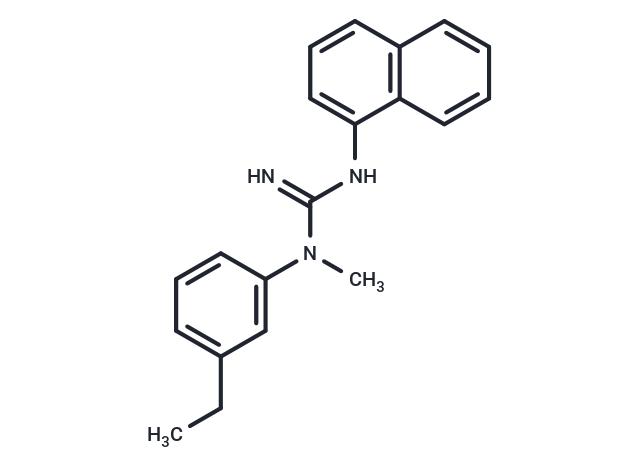
SMILESN=C(NC1=CC=CC=2C=CC=CC21)N(C3=CC=CC(=C3)CC)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Meadows ME, et al. Delayed treatment with a non-competitive NMDA antagonist, CNS-1102 reduces infarct size in rats. Cerebrovasc Dis.1994;4:26-31.
molnova catalog



related products
-
(R)-Serine
(R)-Serine is an endogenous amino acidis a potent co-agonist at the NMDA glutamate receptor.
-
MRZ 2-514
MRZ 2-514 is a strychnine-insensitive modulatory site of the NMDA receptor (glycineB)antagonist with Ki of 33 μM.
-
Glabridin
Glabridin may serve as an anti-inflammatory agent in diabetes-related vascular dysfunction, through regulating the synthesis and activity of iNOS under high-glucose levels.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


