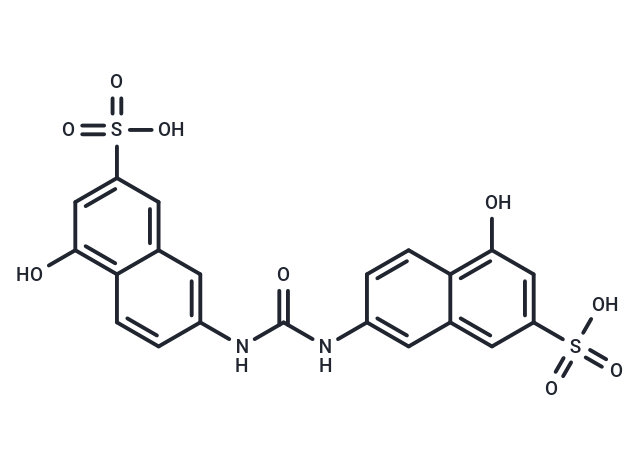
AMI-1 free acid
CAS No. 134-47-4
AMI-1 free acid( —— )
Catalog No. M33795 CAS No. 134-47-4
AMI-1 free acid is a potent, cell-permeable, and reversible inhibitor of protein arginine N-methyltransferases (PRMTs), with inhibitory concentration 50 (IC50) values of 8.8 μM for human PRMT1 and 3.0 μM for yeast-Hmt1p.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 52 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 75 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 184 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 272 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAMI-1 free acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAMI-1 free acid is a potent, cell-permeable, and reversible inhibitor of protein arginine N-methyltransferases (PRMTs), with inhibitory concentration 50 (IC50) values of 8.8 μM for human PRMT1 and 3.0 μM for yeast-Hmt1p.
-
DescriptionAMI-1 free acid is a potent, cell-permeable and reversible inhibitor of protein arginine N-methyltransferases (PRMTs), with IC50s of 8.8 μM and 3.0 μM for human PRMT1 and yeast-Hmt1p, respectively. AMI-1 free acid exerts PRMTs inhibitory effects by blocking peptide-substrate binding.
-
In VitroAMI-1 free acid can inhibit the in vitro methylation reactions performed by all five recombinantly active PRMTs (PRMT1, -3, -4, and -6 and Hmt1p).AMI-1 free acid not only inhibits type I PRMTs (PRMT1, 3, 4 and 6) but also type II PRMT5. AMI-1 free acid specifically inhibits arginine, but not lysine, methyltransferase activity in vitro and does not compete for the AdoMet binding site. AMI-1 free acid inhibits methylation of GFP-Npl3 and cellular proteins.AMI-1 free acid (0.6-2.4 mM; 48-96 hours) inhibits the cell viability of sarcoma in S180 and U2OS cells in a time-dependent and dose-dependent manner in vitro.AMI-1 free acid (1.2-2.4 mM; 48-72 hours) reduces S180 cell viability through the induction of cell apoptosis.Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:S180 cells, U2OS cells Concentration:0.6 mM, 1.2 mM, 2.4 mM Incubation Time:48 hours, 72 hours, 96 hours Result:Inhibited the cell viability.Apoptosis Analysis Cell Line:S180 cellsConcentration:1.2 mM, 2.4 mM Incubation Time:48 hours, 72 hours Result:Increased the percentages of cells undergoing apoptosis.
-
In VivoAMI-1 free acid (0.5 mg; intratumorally; daily; for 7 days) inhibits S180 viability in vivo.AMI-1 free acid (0.5 mg; intratumorally; daily; for 7 days) downregulates PRMT5 but does not regulate the expression of PRMT7 in a tumor xenograft model.AMI-1 free acid (0.5 mg; intratumorally; daily; for 7 days) decreases the levels of H4R3me2s and H3R8me2s in a tumor xenograft model.Animal Model:6-7 weeks old male Kunming mice (18-22 g), with S180 cells xenograft Dosage:0.5 mg Administration: Intratumorally, daily, for 7 days Result:Decreased tumor weight.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorHistone Methyltransferase
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number134-47-4
-
Formula Weight504.49
-
Molecular FormulaC21H16N2O9S2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 83.33 mg/mL (165.18 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESO=C(NC=1C=CC2=C(O)C=C(C=C2C1)S(=O)(=O)O)NC=3C=CC4=C(O)C=C(C=C4C3)S(=O)(=O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Zhang, B., et al. Targeting protein arginine methyltransferase 5 inhibits colorectal cancer growth by decreasing arginine methylation of eIF4E and FGFR3. Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 8;6(26):22799-811.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Aristolochic acid D
Aristolochic acid D is an aristolochic acid derivative isolated from stems of Aristolochia indica. Aristolochic acid is nephrotoxin and carcinogen.
-
Dendrobine
Dendrobine has a slight but demonstrable analgesic and antipyretic action.Dendrobine produces moderate hyperglycemia, diminishes cardiac activity in large doses, lowers the blood pressure.
-
Lactose b
Lactose is the major sugar present in milk and the main source of energy supplied to the newborn mammalian in its mother's milk. Lactose is also an important osmotic regulator of lactation.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


