 Home -
Products -
Proteasome/Ubiquitin -
Endogenous Metabolite -
D-Glucose 6-phosphate disodium salt
Home -
Products -
Proteasome/Ubiquitin -
Endogenous Metabolite -
D-Glucose 6-phosphate disodium salt
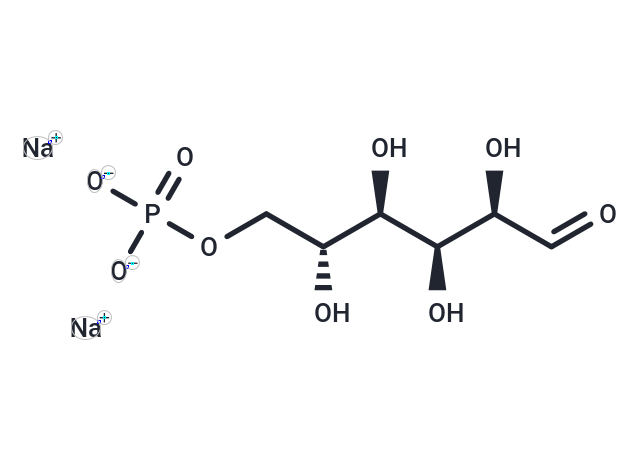
D-Glucose 6-phosphate disodium salt
CAS No. 3671-99-6
D-Glucose 6-phosphate disodium salt( —— )
Catalog No. M33594 CAS No. 3671-99-6
D-Glucose 6-phosphate disodium salt is a compound widely present in biological systems. It is a molecule formed when glucose undergoes phosphorylation at the 6th carbon.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 33 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 50 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 72 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameD-Glucose 6-phosphate disodium salt
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionD-Glucose 6-phosphate disodium salt is a compound widely present in biological systems. It is a molecule formed when glucose undergoes phosphorylation at the 6th carbon.
-
DescriptionD-Glucose-6-phosphate disodium salt is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number3671-99-6
-
Formula Weight304.1
-
Molecular FormulaC6H11Na2O9P
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 250 mg/mL (822.10 mM; Ultrasonic)
-
SMILES[Na+].[Na+].O[C@H](COP([O-])([O-])=O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Olsen BB, et al. Linked Hexokinase and Glucose-6-Phosphatase Activities Reflect Grade of Ovarian Malignancy. Mol Imaging Biol. 2018 Jul 9.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
DL-Homocysteine
DL-Homocysteine is a potential marker for tumor cell growth. increased plasma homocysteine is a risk factor for coronary heart disease and carcinogenesis.
-
Nervonic acid
Nervonic acid is a long chain unsaturated fatty acid that is enriched in sphingomyelin. It consists of choline sphingosine phosphoric acid and fatty acid.
-
3-Hydroxybutyric aci...
3-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium (β-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium) is a metabolite found in type I diabetic patients that regulates membrane lipids.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com

