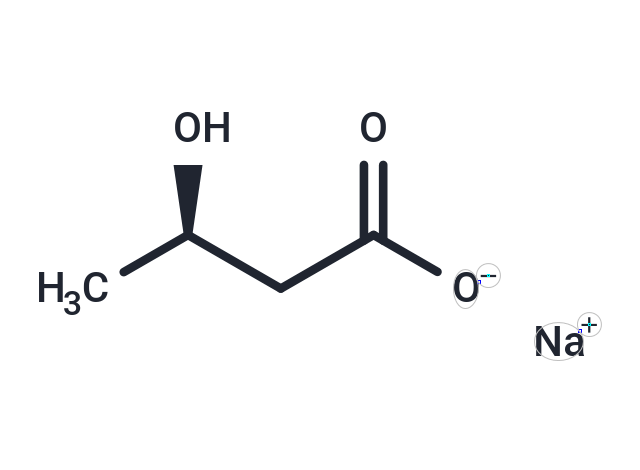
3-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium
CAS No. 150-83-4
3-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium( —— )
Catalog No. M35854 CAS No. 150-83-4
3-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium (β-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium) is a metabolite found in type I diabetic patients that regulates membrane lipids.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 28 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name3-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description3-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium (β-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium) is a metabolite found in type I diabetic patients that regulates membrane lipids.
-
Description3-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium (β-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium) is a metabolite that is elevated in type I diabetes. 3-Hydroxybutyric acid sodium can modulate the properties of membrane lipids.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number150-83-4
-
Formula Weight126.09
-
Molecular FormulaC4H7NaO3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 25 mg/mL (198.27 mM; Ultrasonic (<60°C) DMSO : 16.67 mg/mL (132.21 mM; Ultrasonic (<60°C)
-
SMILES[Na+].C[C@@H](O)CC([O-])=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Hsu TT, et al. 3-Hydroxybutyric acid interacts with lipid monolayers at concentrations that impair consciousness. Langmuir. 2013 Feb 12;29(6):1948-55.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Estetrol
Estetrol(Donesta) is an orally available, selective modulator of the estrogen receptor, a naturally occurring estrogen synthesized by the human fetal liver during pregnancy.
-
Cyclopentanone
Cyclopentanone is found in animal foods.
-
L-Kynurenine
L-Kynurenine is a key intermediate in the breakdown pathway of tryptophan. L-Kynurenine is a substrate of kynureninase KMO and KAT associated with the suppression of antitumor immune responses.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


