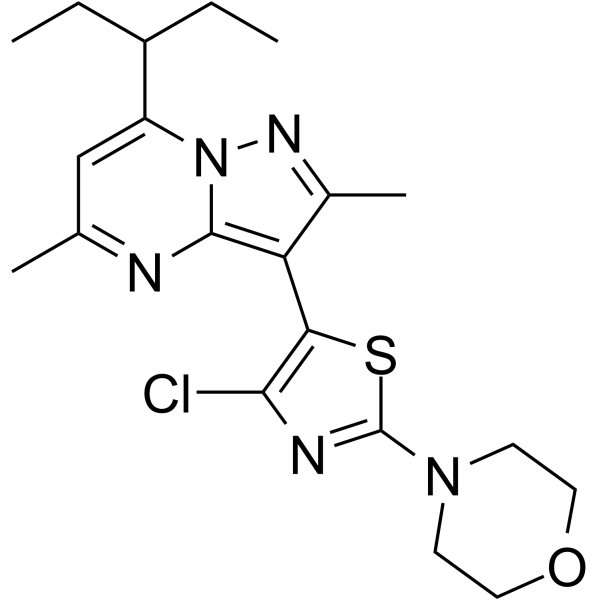
Tildacerfont
CAS No. 1014983-00-6
Tildacerfont( —— )
Catalog No. M27834 CAS No. 1014983-00-6
Tildacerfont is an antagonist of CRF1 and reduces the levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone and adrenal androgen. Tildacerfont can be used in studies about congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 45 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 63 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameTildacerfont
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionTildacerfont is an antagonist of CRF1 and reduces the levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone and adrenal androgen. Tildacerfont can be used in studies about congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
-
DescriptionTildacerfont is an antagonist of CRF1 and reduces the levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone and adrenal androgen. Tildacerfont can be used in studies about congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetCRF Receptor
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1014983-00-6
-
Formula Weight419.97
-
Molecular FormulaC20H26ClN5OS
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 10 mg/mL (23.81 mM)
-
SMILESCCC(CC)c1cc(C)nc2c(c(C)nn12)-c1sc(nc1Cl)N1CCOCC1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Uhlenheuer DA, et al. Cucurbit[8]uril induced heterodimerization of methylviologen and naphthalene functionalized proteins. Chem Commun (Camb). 2011;47(24):6798-6800.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Verucerfont
Verucerfont is an antagonist of corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 (CRF1) .
-
CP 316311
CP 316311 is a specific CRF1 receptor antagonist with potential antidepressant activity and may be used in the study of depression.
-
Urocortin III, mouse
Mouse UcnIII is expressed predominantly in regions of the brain known to be involved in stress-related behaviours, and its expression in the hypothalamus increases following restraint.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


