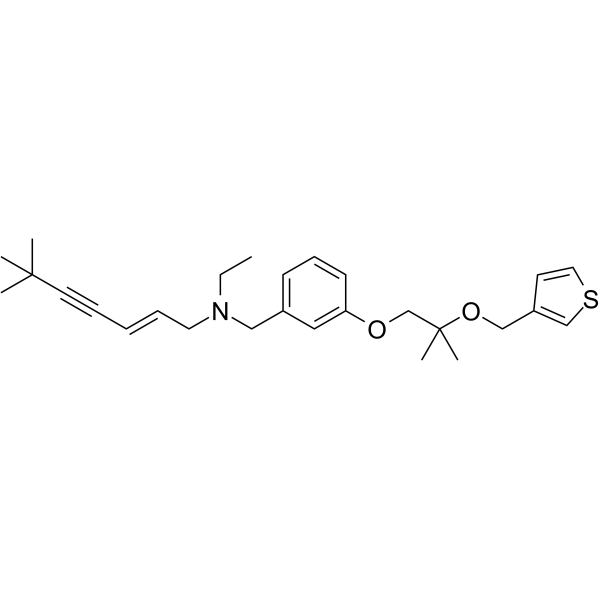
FR194738 free base
CAS No. 204067-45-8
FR194738 free base( —— )
Catalog No. M26220 CAS No. 204067-45-8
FR194738 inhibits squalene epoxidase activity in HepG2 cell homogenates with an IC50 of 9.8 nM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 187 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 170 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 247 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 387 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 509 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 658 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameFR194738 free base
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionFR194738 inhibits squalene epoxidase activity in HepG2 cell homogenates with an IC50 of 9.8 nM.
-
DescriptionFR194738 inhibits squalene epoxidase activity in HepG2 cell homogenates with an IC50 of 9.8 nM. FR194738 free base is a squalene epoxidase inhibitor.(In Vitro):FR194738 free base potently inhibits squalene epoxidase in HepG2 cell homogenate and liver microsomes in dogs and rats. FR194738 free base inhibits hamster liver microsomal squalene epoxidase activity in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 of 14 nM. In intact HepG2 cells, FR194738 free base inhibits the incorporation of [14C]acetate into free cholesterol and cholesteryl ester in a concentration-dependent manner(IC50s = 4.9 and 8.0 nM). FR194738 free base induces intracellular [14C]squalene accumulation and increases the incorporation of [14C]acetate into squalene.(In Vivo):FR194738 free base reduces the serum levels of total, non high density lipoprotein and high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglyceride. In hamsters, FR194738 free base(32 mg/kg) increases HMG-CoA reductase activity by 1.3-fold.
-
In VitroIn intact HepG2 cells, FR194738 concentration-dependently inhibits the incorporation of [14C]acetate into free cholesterol and cholesteryl ester, with IC50s of 4.9 and 8.0 nM, respectively. FR194738 induces intracellular [14C]squalene accumulation. FR194738 increases the incorporation of [14C]acetate into squalene, an intermediate of cholesterol synthesis. FR194738 potently inhibits squalene epoxidase (SE) in HepG2 cell homogenate and liver microsomes in dogs and rats. The inhibitory effect of FR194738 in comparison to the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, Simvastatin, Fluvastatin and Pravastatin, on cholesterol biosynthesis in HepG2 cells is examined. Among these compounds, FR194738 is the most potent, with an IC50 of 2.1 nM. The IC50s of Simvastatin, Fluvastatin and Pravastatin are 40, 28 and 5100 nM, respectively. FR194738 inhibits hamster liver microsomal squalene epoxidase activity in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 of 14 nM.
-
In VivoSerum lipid levels in hamsters after daily administration of FR194738 and Pravastatin for 10 d are measured. FR194738 reduces the serum levels of total, non high density lipoprotein (HDL) and HDL cholesterol, and triglyceride. Treatment of hamsters with FR194738 increases HMG-CoA reductase activity by 1.3-fold at 32 mg/kg compared to the control group and does not significantly change that at 100 mg/kg.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number204067-45-8
-
Formula Weight439.66
-
Molecular FormulaC27H37NO2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (227.45 mM)
-
SMILESCCN(C\C=C\C#CC(C)(C)C)Cc1cccc(OCC(C)(C)OCc2ccsc2)c1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Wang X, Wang D, Zhou Z, Zhu W. Subacute oral toxicity assessment of benalaxyl in mice based on metabolomics methods. Chemosphere. 2018 Jan;191:373-380.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Tildipirosin
Tildipirosin is a 16-membered macrolide used as an antibiotic in veterinary medicine. Like other macrolides it inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria and blocks the production of biofilms.
-
Finafloxacin
Finafloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic that demonstrates superior activity to ciprofloxacin under acidic conditions (pH5.8, A. baumannii isolates MIC=0.03-0.12ug/mL).
-
Phenazine-1-carboxyl...
Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid shows strong antifungal activity against all phytopathogenic fungi, inhibiting the fungal growth by about 90-100%. Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid could be used to compete with other phytopathogenic fungi that attack grapevine



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


