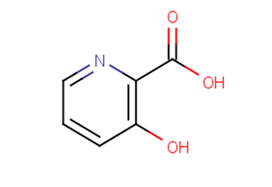
3-Hydroxypicolinic acid
CAS No. 874-24-8
3-Hydroxypicolinic acid( Picolinic acid 3-hydroxy- (6CI7CI8CI) | 2-Carboxy-3-hydroxypyridine )
Catalog No. M20615 CAS No. 874-24-8
3-Hydroxypicolinic acid is a picolinic acid derivative and belongs to the pyridine family.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name3-Hydroxypicolinic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description3-Hydroxypicolinic acid is a picolinic acid derivative and belongs to the pyridine family.
-
Description3-Hydroxypicolinic acid is a picolinic acid derivative and belongs to the pyridine family.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsPicolinic acid 3-hydroxy- (6CI7CI8CI) | 2-Carboxy-3-hydroxypyridine
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number874-24-8
-
Formula Weight139.11
-
Molecular FormulaC6H5NO3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:28 mg/mL (201.27 mM)
-
SMILESOC(=O)c1ncccc1O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Tang K Taranenko N I Allman S L et al. Picolinic acid as a matrix for laser mass spectrometry of nucleic acids and proteins[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 1994 8(9):673-677.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Angiotensin III, hum...
Angiotensin III is an agonist of angiotensin 1 (AT1) and AT2 receptor.
-
Sphingomyelin
Sphingomyelin is a natural sphingolipid that existed in animal cell membranes. It implicates the regulation of transmembrane signaling.
-
Pyridoxylamine
Pyridoxylamine is an inhibitor of advanced glycation end production (AGEs) and lipoxidation end products (ALEs).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


