SC-66
CAS No. 871361-88-5
SC-66( SC66 | SC 66 )
Catalog No. M16333 CAS No. 871361-88-5
SC66 is an allosteric Akt inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 53 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 92 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 141 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 206 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 513 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSC-66
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSC66 is an allosteric Akt inhibitor.
-
DescriptionSC66 is an allosteric Akt inhibitor; exhibits a dual inhibitory activity that directly interferes with the PH domain binding to PIP3 and facilitates Akt ubiquitination; has anticancer activity mouse xenograft tumor model.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsSC66 | SC 66
-
PathwayCytoskeleton/Cell Adhesion Molecules
-
TargetAkt
-
RecptorAkt
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number871361-88-5
-
Formula Weight276.3324
-
Molecular FormulaC18H16N2O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: ≥ 34 mg/mL
-
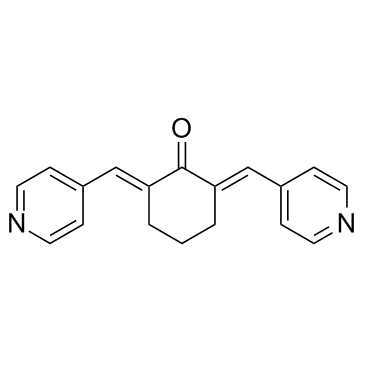
SMILESO=C1/C(CCC/C1=C\C2=CC=NC=C2)=C/C3=CC=NC=C3
-
Chemical NameCyclohexanone, 2,6-bis(4-pyridinylmethylene)-, (2E,6E)-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Jo H, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Apr 19;108(16):6486-91.
2. Cusimano A, et al. Oncotarget. 2015 Jan 30;6(3):1707-22.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Crosstide
Crosstide is a peptide analog of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) that functions as a natural substrate for Akt/PKB.
-
Ipatasertib dihydroc...
Ipatasertib dihydrochloride is a highly selective and ATP-competitive inhibitor of pan-Akt (IC50s: 5, 18 and 8 nM for Akt1, Akt2 and Akt3, respectively).
-
Marein
Marein shows neuroprotective effect on PC12 cell damage induced by methylglyoxal, which is due to a reduction of damage to mitochondria function and activation of the AMPK signal pathway.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


