Lartesertib
CAS No. 2495096-26-7
Lartesertib( —— )
Catalog No. M35661 CAS No. 2495096-26-7
Lartesertib (ATM Inhibitor-5) is an inhibitor of serine/threonine protein kinase ATM with potential anticancer activity for the study of lung cancer.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 201 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 312 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 534 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 1003 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1674 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 2538 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLartesertib
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLartesertib (ATM Inhibitor-5) is an inhibitor of serine/threonine protein kinase ATM with potential anticancer activity for the study of lung cancer.
-
DescriptionLartesertib (M4076) is a potent inhibitor of serine/threonine protein kinase ATM (extracted from patent WO2022058351A1).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetATM/ATR
-
RecptorATM/ATR
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2495096-26-7
-
Formula Weight448.45
-
Molecular FormulaC23H21FN6O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (222.99 mM)
-
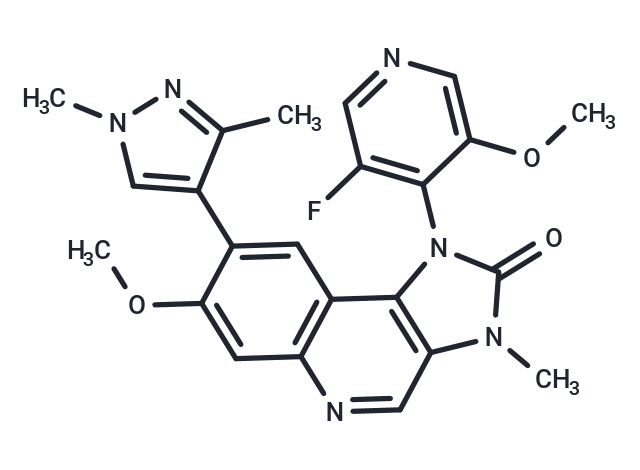
SMILESCOc1cncc(F)c1-n1c2c(cnc3cc(OC)c(cc23)-c2cn(C)nc2C)n(C)c1=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Alessandra AMBRUOSI, et al. Pharmaceutical preparation. WO2022058351A1.
molnova catalog



related products
-
KU-60019 (b)
KU-60019 is an improved analogue of KU-55933, with IC50 of 6.3 nM for ATM in cell-free assays.
-
KU-55933
KU-55933 is a potent, specific, ATP-competitive inhibitor of ATM with Ki/IC50 of 2.2/13 nM.
-
KU-60019
KU-60019 is an improved analogue of KU-55933, and is a potent, specific inhibitor of ATM kinase with IC50 of 6.3 nM, 270- and 1,600-fold selectivity over DNA-PKcs and ATR.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


