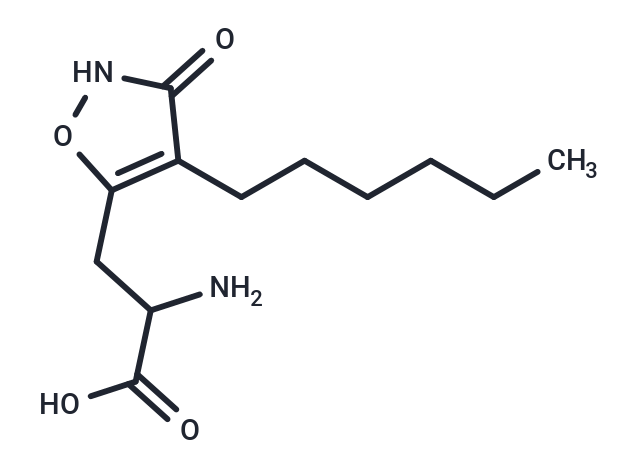
HexylHIBO
CAS No. 334887-43-3
HexylHIBO( —— )
Catalog No. M33866 CAS No. 334887-43-3
HexylHIBO is a type I mGluR antagonist that inhibits mGlu1a and mGlu5a, with Kb values of 140 and 110 μM, respectively.HexylHIBO decreases sEPSC in rats.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 117 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 169 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 250 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 547 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameHexylHIBO
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionHexylHIBO is a type I mGluR antagonist that inhibits mGlu1a and mGlu5a, with Kb values of 140 and 110 μM, respectively.HexylHIBO decreases sEPSC in rats.
-
DescriptionHexylHIBO is a potent group I mGluR antagonist with Kbs of 140 and 110 μM at mGlu1a and mGlu5a receptors, respectively. HexylHIBO decreased sEPSC in rat.
-
In VitroThus ambient levels of glutamate tonically activate mGluRs and regulate cortical excitability.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayNeuroscience
-
TargetGluR
-
RecptorGluR
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number334887-43-3
-
Formula Weight256.3
-
Molecular FormulaC12H20N2O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESC(CCCCC)C1=C(CC(C(O)=O)N)ONC1=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Madsen U, et al. Synthesis and pharmacology of 3-isoxazolol amino acids as selective antagonists at group I metabotropic glutamic acid receptors. J Med Chem. 2001;44(7):1051-1059.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Dipraglurant
Dipraglurant (ADX48621) is a negative alteration modulator (NAM) of mGluR5 that inhibits dyskinesia in the LID macaque model.
-
GYKI 53655 hydrochlo...
GYKI 53655 hydrochloride (LY300168 hydrochloride) is an antagonist of AMPA and is used in the study of neurological disorders.
-
FPTQ
FPTQ is an antagonist of mGluR1.FPTQ is a synthetic isoquinoline derivative.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


