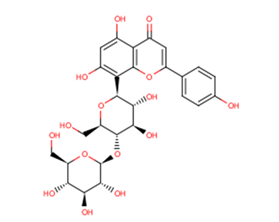
Vitexin 4-O-glucoside
CAS No. 178468-00-3
Vitexin 4-O-glucoside( ——— )
Catalog No. M38636 CAS No. 178468-00-3
Vitexin-4''-O-glucoside is a kind of flavonoid fraction from the leaves of Crataegus pinnatifida.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 67 | In Stock |


|
| 2MG | 29 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 44 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 60 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameVitexin 4-O-glucoside
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionVitexin-4''-O-glucoside is a kind of flavonoid fraction from the leaves of Crataegus pinnatifida.
-
DescriptionVitexin 4''-O-glucoside
-
In Vitro———
-
In Vivo———
-
Synonyms———
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor———
-
Research Area———
-
Indication———
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number178468-00-3
-
Formula Weight594.52
-
Molecular FormulaC27H30O15
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : 100 mg/mL (168.20 mM; ultraphonic )
-
SMILESOC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O[C@@H]2[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@H]2O)c2c(O)cc(O)c3c2oc(cc3=O)-c2ccc(O)cc2)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Lei Wen, et al. An Efficient Method for the Preparative Isolation and Purification of Flavonoids From Leaves of Crataegus Pinnatifida by HSCCC and Pre-HPLC. Molecules. 2017 May 9;22(5):767.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Clausemargic A
Clausemargic A
-
BC-1471
BC-1471 is a STAM-binding protein (STAMBP) deubiquitinase inhibitor that inhibits the inflammasome activity of NALP7 (NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 7) .
-
Lithium potassium ac...
Acetyl phosphate is a compound involved in taurine and hypotaurine metabolism as well as pyruvate metabolism. It is generated from sulfoacetaldehyde converted to acetyl-CoA and acetate via phosphate acetyltransferase and acetate kinase respectively. It is also an intermediate in pyruvate metabolism.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


