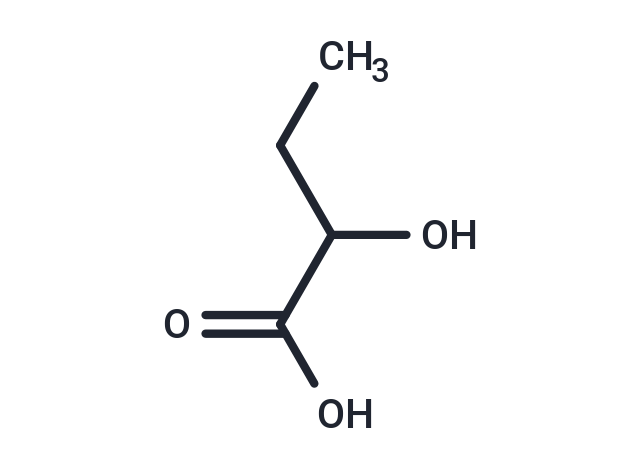
2-Hydroxybutyric acid
CAS No. 600-15-7
2-Hydroxybutyric acid( —— )
Catalog No. M35282 CAS No. 600-15-7
2-Hydroxybutyric acid (α-Hydroxybutyric acid) is a product of protein metabolism and serves as a biomarker for type 2 diabetes and pre-eclampsia.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 33 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 105 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 152 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-Hydroxybutyric acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2-Hydroxybutyric acid (α-Hydroxybutyric acid) is a product of protein metabolism and serves as a biomarker for type 2 diabetes and pre-eclampsia.
-
Description2-Hydroxybutyric acid (α-Hydroxybutyric acid ) is converted from 2-Aminobutyric acid, with 2-oxobutyric acid as an intermediate metabolite.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number600-15-7
-
Formula Weight104.1
-
Molecular FormulaC4H8O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (960.61 mM; Ultrasonic (<50°C)
-
SMILESCCC(O)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Landaas S, et al. The formation of 2-hydroxybutyric acid in experimental animals. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Jan 6;58(1):23-32.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
2′-Deoxyadenosine 5′...
2′-Deoxyadenosine 5′-monophosphate disodium, a nucleic acid AMP derivative, is a deoxyribonucleotide found in DNA. 2′-Deoxyadenosine 5′-monophosphate disodium can be used to study adenosine-based interactions during DNA synthesis and DNA damage.
-
4-Methylbiphenyl
4-Methylbiphenyl is an endogenous metabolite.
-
N-Acetylhistamine
N-Acetylhistamine is a metabolite of histamine.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


