ADR-925
CAS No. 75459-34-6
ADR-925( —— )
Catalog No. M34491 CAS No. 75459-34-6
ADR-925, an active chelated iron metabolite of dexrazoxane, has the ability to protect neonatal rat cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin-induced injury.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 2138 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 2822 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 4266 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 5552 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameADR-925
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionADR-925, an active chelated iron metabolite of dexrazoxane, has the ability to protect neonatal rat cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin-induced injury.
-
DescriptionADR-925, an active chelated iron metabolite of dexrazoxane, has the ability to protect neonatal rat cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin-induced injury.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number75459-34-6
-
Formula Weight304.3
-
Molecular FormulaC11H20N4O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
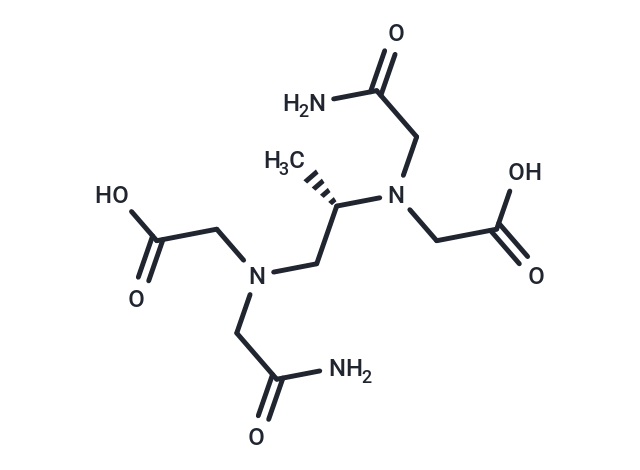
SMILESN([C@H](CN(CC(N)=O)CC(O)=O)C)(CC(N)=O)CC(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Oxoadipic acid
Oxoadipic acid is a key metabolite of the essential amino acids tryptophan and lysine.Important metabolite between the TCA cycle and lysine biosynthesis. Of interest for research on mitochondrial metabolite transporters.
-
Phenylacetic acid
Phenyl acetate (or phenylacetate) is a carboxylic acid ester that has been found in the biofluids of patients with nephritis and/or hepatitis as well as patients with phenylketonuria (PKU) an inborn error of metabolism. Excess phenylalanine in the body can be disposed of through a transamination process leading to the production of phenylpyruvate.
-
Dodecanoylcarnitine
Dodecanoylcarnitine ((-)-Lauroylcarnitine) has been associated with disturbances in fatty acid oxidation, and the use of Dodecanoylcarnitine resulted in an increase in the permeability of salmon calcitonin.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


