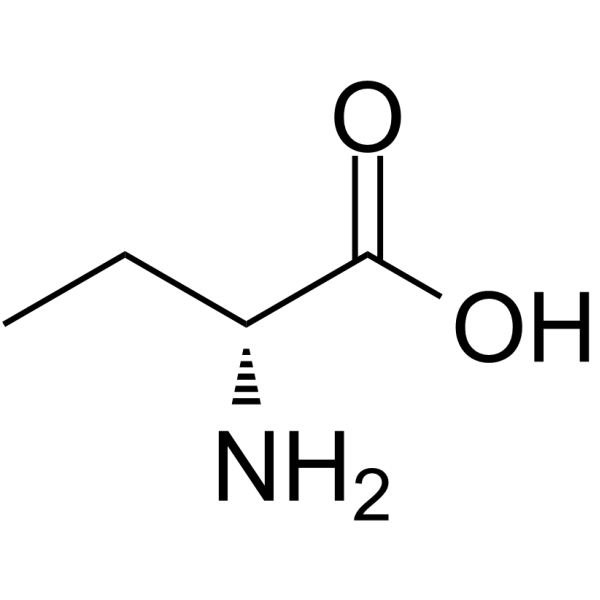
D(-)-2-Aminobutyric acid
CAS No. 2623-91-8
D(-)-2-Aminobutyric acid( —— )
Catalog No. M27073 CAS No. 2623-91-8
D(-)-2-Aminobutyric acid is the substrate of D-amino acid oxidase.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 27 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameD(-)-2-Aminobutyric acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionD(-)-2-Aminobutyric acid is the substrate of D-amino acid oxidase.
-
DescriptionD(-)-2-Aminobutyric acid is the substrate of D-amino acid oxidase.(In Vitro):D(-)-2-Aminobutyric acid (D-α-aminobutyric acid) is a substrate of D-amino acid oxidase.
-
In VitroD(-)-2-Aminobutyric acid (D-α-aminobutyric acid) is a substrate of D-amino acid oxidase.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2623-91-8
-
Formula Weight103.121
-
Molecular FormulaC4H9NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 100 mg/mL (969.74 mM)
-
SMILESCC[C@@H](N)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Zhao F, et al. Natural Sources and Bioactivities of 2,4-Di-Tert-Butylphenol and Its Analogs. Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jan 6;12(1):35.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Palmitoyl CoA lithiu...
Palmitoyl CoA lithium (Palmitoyl coenzyme A lithium) is a major component of fatty acids involved in the carnitine shuttle system, beta-oxidation, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and can be used to study metabolic disorders in the body.
-
Isolithocholic Acid
Isolithocholic Acid (3-Epilithocholic acid) (β-Lithocholic acid) is an isomer of Lithocholic acid.
-
Farnesol
Farnesol is a natural product has the activity in inhibiting bacteria.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


