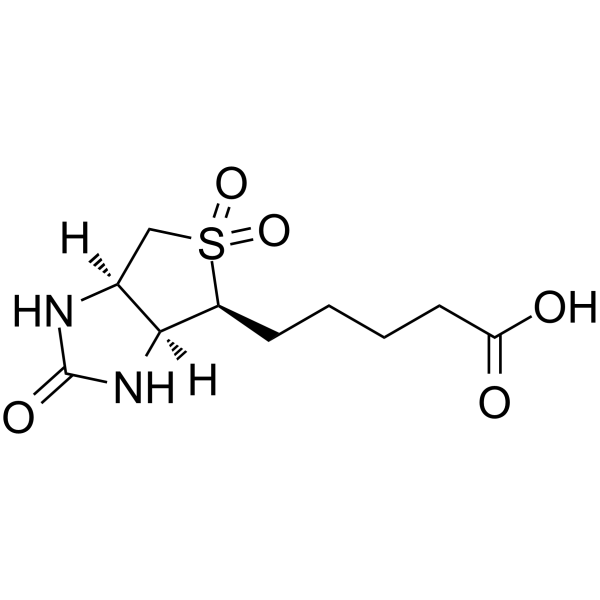
Biotin sulfone
CAS No. 40720-05-6
Biotin sulfone( —— )
Catalog No. M26551 CAS No. 40720-05-6
Biotin sulfone is an oxidized form of biotin.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 28 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 44 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 63 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBiotin sulfone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBiotin sulfone is an oxidized form of biotin.
-
DescriptionBiotin sulfone is an oxidized form of biotin.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorAP-1| HIV-1 protease| IFN-γ| IL-17A| MAPK| NF-κB| TNF-α
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number40720-05-6
-
Formula Weight276.31
-
Molecular FormulaC10H16N2O5S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 250 mg/mL (904.78 mM)
-
SMILESOC(=O)CCCC[C@H]1[C@H]2NC(=O)N[C@H]2CS1(=O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Liu C, et al. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Ganoderma lucidum Triterpenoid in Human Crohn's Disease Associated with Downregulation of NF-κB Signaling. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015 Aug;21(8):1918-25.
molnova catalog



related products
-
2-Ethylpyrazine
2-Ethylpyrazine is present in roasted coffee beans and is a volatile compound .2-Ethylpyrazine induces vasodilation through the activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factors.
-
Octadecanedioic acid
Octadecanedioic acid is an endogenous metabolite, is a long-chain dicarboxylic acid.
-
L-(+)-Arabinose
L-(+)-Arabinose inhibits intestinal sucrase activity, thereby reducing sucrose utilization, and consequently decreasing lipogenesis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


