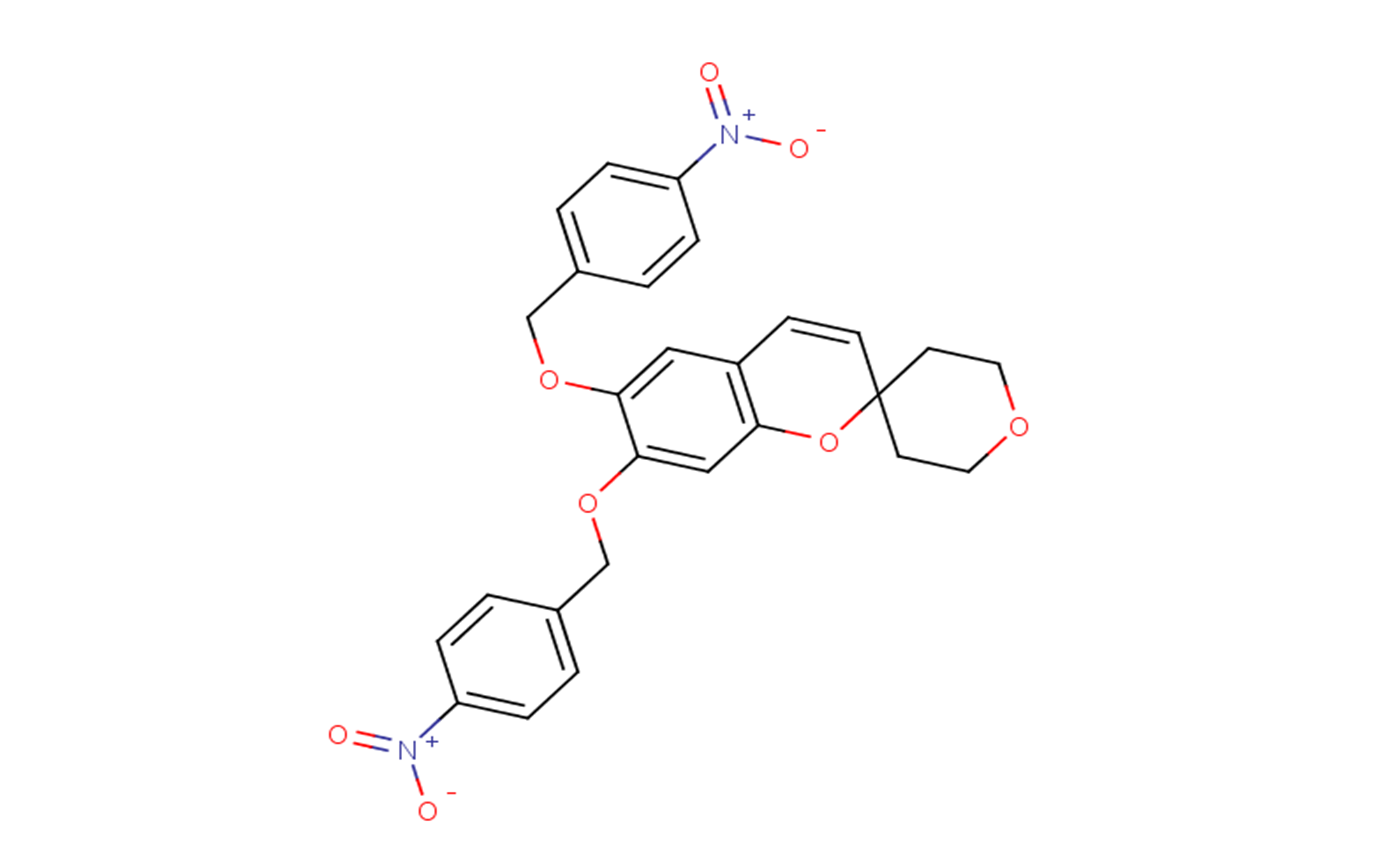
CU-CPT17e
CAS No. 2109805-75-4
CU-CPT17e( —— )
Catalog No. M23960 CAS No. 2109805-75-4
CU-CPT17e is a potent agonist of TLR(TLR3, TLR8, and TLR9).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 419 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 617 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 938 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1293 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1739 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCU-CPT17e
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCU-CPT17e is a potent agonist of TLR(TLR3, TLR8, and TLR9).
-
DescriptionCU-CPT17e is a potent agonist of TLR(TLR3, TLR8, and TLR9).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayImmunology/Inflammation
-
TargetTLR
-
RecptorTLR3|TLR8|TLR9
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2109805-75-4
-
Formula Weight504.49
-
Molecular FormulaC27H24N2O8
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM (Need ultrasonic and warming)
-
SMILESO=[N+]([O-])C(C=C1)=CC=C1COC2=CC(C=CC3(CCOCC3)O4)=C4C=C2OCC5=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C5
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Zhang L, et al. Discovery of Small Molecules as Multi-Toll-like Receptor Agonists with Proinflammatory and Anticancer Activities. J Med Chem. 2017 Jun 22;60(12):5029-5044.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Okanin
Okanin shows significant activities on both linoleic acid peroxidation inhibition and DPPH radical scavenging effect.
-
CU-CPT9b
CU-CPT9b is an antagonist of toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8;?Kd = 21 nM).?It inhibits activation of NF-?B induced by the TLR8 agonist R-848 in TLR8-overexpressing HEK-Blue cells with an IC50 value of 0.7 nM.
-
SM360320
SM360320 is an effective and selective agonist of TLR7. SM360320 inhibits HCV replication in hepatocytes via a type I IFN-independent mechanism in addition to its IFN-mediated activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


