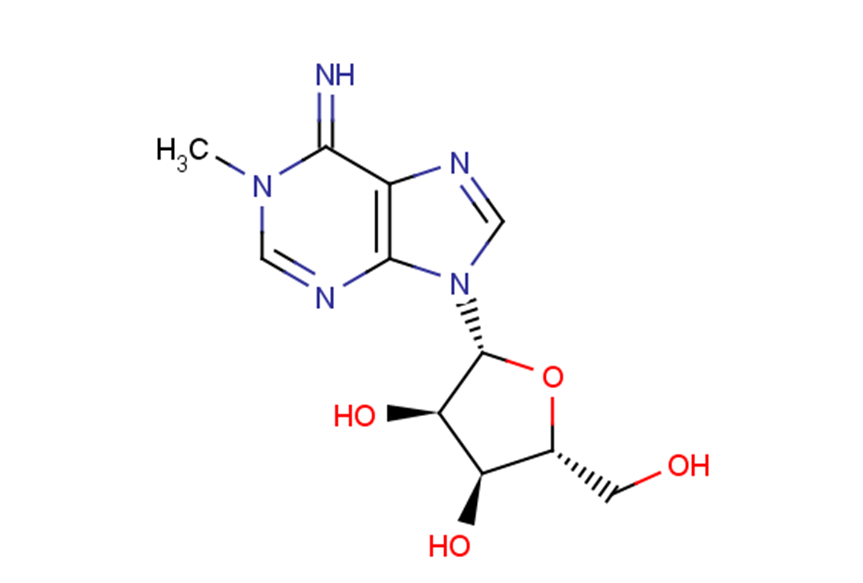
1-Methyladenosine
CAS No. 15763-06-1
1-Methyladenosine( —— )
Catalog No. M22280 CAS No. 15763-06-1
1-Methyladenosine (M1A) belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine nucleosides.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 31 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 44 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 63 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name1-Methyladenosine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description1-Methyladenosine (M1A) belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine nucleosides.
-
Description1-Methyladenosine (M1A) belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine nucleosides.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number15763-06-1
-
Formula Weight281.27
-
Molecular FormulaC11H15N5O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:145 mg/mL (515.52 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESCN(C=Nc1c2ncn1[C@@H]([C@@H]1O)O[C@H](CO)[C@H]1O)C2=N
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Hauenschild R, et al. The reverse transcription signature of N-1-methyladenosine in RNA-Seq is sequence dependent. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Nov 16;43(20):9950-64.
molnova catalog



related products
-
2-Hydroxybutyric aci...
2-Hydroxybutyric acid (α-Hydroxybutyric acid) is a product of protein metabolism and serves as a biomarker for type 2 diabetes and pre-eclampsia.
-
Indole-3-carboxylic ...
Indole-3-carboxylic acid is a normal urinary indolic tryptophan metabolite .
-
Cholesteryl oleate
Cholesteryl oleate is a cholesteryl ester. Cholesteryl oleate can be used to synthesize solid lipid nanoparticles which is a nanoparticle-based gene therapy approach.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


