EML 425
CAS No. 1675821-32-5
EML 425( —— )
Catalog No. M22069 CAS No. 1675821-32-5
EML 425 is a potent and selective inhibitor of CREB binding protein (CBP)/p300 (IC50s: 2.9 and 1.1 μM, respectively).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 39 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 62 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 131 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 193 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 286 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 405 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameEML 425
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionEML 425 is a potent and selective inhibitor of CREB binding protein (CBP)/p300 (IC50s: 2.9 and 1.1 μM, respectively).
-
DescriptionEML 425 is a potent and selective inhibitor of CREB binding protein (CBP)/p300 (IC50s: 2.9 and 1.1 μM, respectively). EML 425 is shown to be a reversible inhibitor, noncompetitive versus both acetyl-CoA and a histone H3 peptide, and able to bind both the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex, even with unequal affinity constants. EML 425, noncompetitive versus both acetyl-CoA and a histone H3 peptide, shows good cell permeability. EML 425 inhibits both p300 and CBP (IC50 values of 2.9 and 1.1 μM, respectively) while being practically inactive against the enzymes general control non-derepressible-5 (GCN5) and p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF). EML 425 causes a marked and time-dependent reduction in the acetylation of lysine H4K5 and H3K9 in U937 cells. The binding site for EML 425 is an alternative pocket lying near the substrate lysine binding groove and close to the acetylation site.
-
In VitroEML 425 (EML425, Compound 7h) is a potent and selective reversible inhibitor of CBP/p300, noncompetitive versus both acetyl-CoA and a histone H3 peptide, and endows with good cell permeability. EML 425 inhibits both p300 and CBP (IC50 values of 2.9 and 1.1 μM, respectively) while being practically inactive against the enzymes general control non derepressible-5 (GCN5) and p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF). EML 425 induces a marked and time-dependent reduction in the acetylation of lysine H4K5 and H3K9 in U937 cells. EML 425 is shown to be a reversible inhibitor, noncompetitive versus both acetyl-CoA and a histone H3 peptide, and able to bind both the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex, even with unequal affinity constants. The best scoring docking poses suggest that the binding site for EML 425 is an alternative pocket lying near the substrate lysine binding groove and close to the acetylation site.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetEpigenetic Reader Domain
-
Recptorp300|CBP
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1675821-32-5
-
Formula Weight440.49
-
Molecular FormulaC27H24N2O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:250 mg/mL (567.55 mM)
-
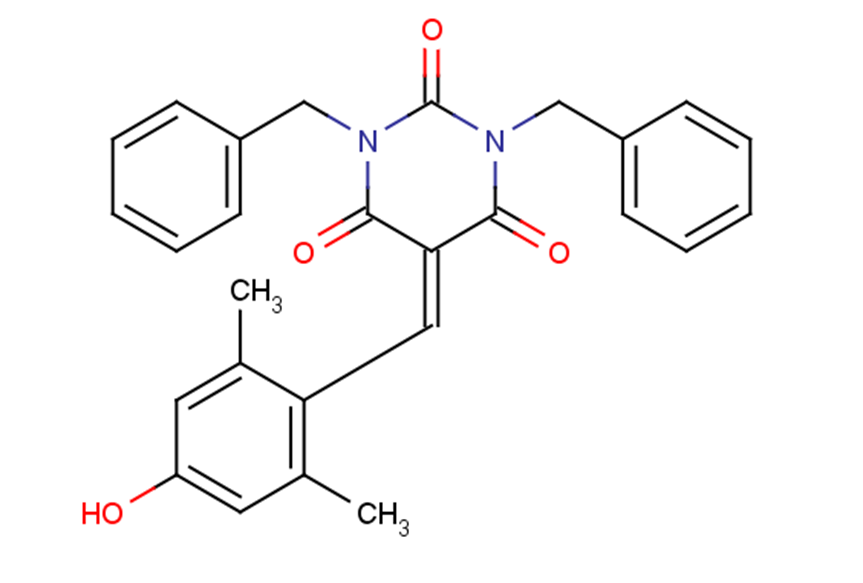
SMILESCC1=CC(O)=CC(C)=C1C=C1C(=O)N(CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)N(CC2=CC=CC=C2)C1=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Milite C, et al. A novel cell-permeable, selective, and noncompetitive inhibitor of KAT3 histone acetyltransferases from a combined molecular pruning/classical isosterism approach. J Med Chem. 2015 Mar 26;58(6):2779-98.
molnova catalog



related products
-
SGC-SMARCA-BRDVIII
SGC-SMARCA-BRDVIII is a potent and selective inhibitor of SMARCA2, SMARCA4, PB1(2), PB1(3) and PB1(5) with Kds of 35 nM, 36 nM, 3.7 μM, 2.0 μM and 13 nM, respectively.
-
ZEN-3411
ZEN-3411 is an orally available and potent BET inhibitor that inhibits BRD4(BD1), BRD4(BD2), and BRD4(BD1BD2) and suppresses the growth of tumor cells overproducing BET proteins.
-
PBRM1-BD2-IN-5
PBRM1-BD2-IN-5 is a potent inhibitor of the PBRM1 Bromodomain, with dissociation constant (Kd) values of 1.5 μM and 3.9 μM for PBRM1-BD2 and PBRM1-BD5 respectively, and an inhibitory concentration 50 (IC50) value of 0.26 μM for PBRM1-BD2.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


