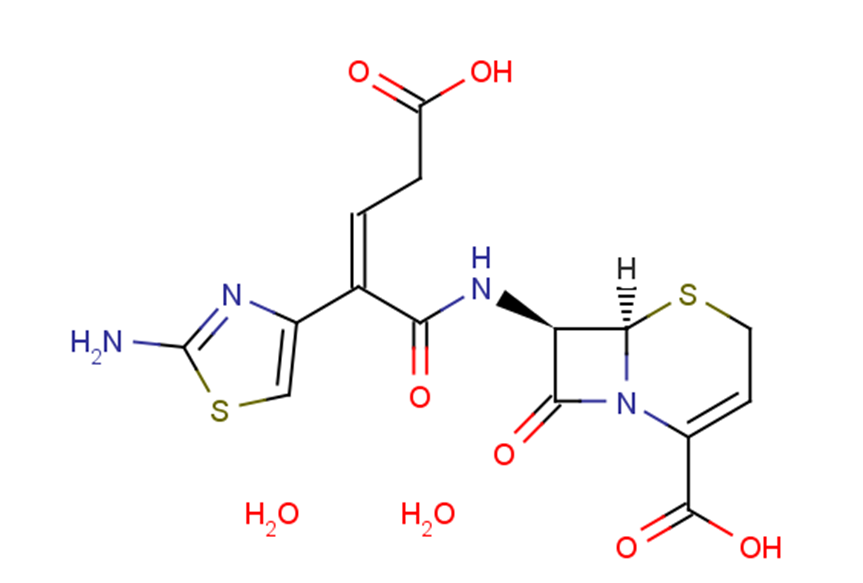
Ceftibuten dihydrate
CAS No. 118081-34-8
Ceftibuten dihydrate( Sch-39720 dihydrate )
Catalog No. M22032 CAS No. 118081-34-8
Ceftibuten dihydrate is the dihydrate form of ceftibuten, and is a third-generation cephalosporin with antibacterial activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 48 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 29 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 78 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 117 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 174 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 431 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCeftibuten dihydrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCeftibuten dihydrate is the dihydrate form of ceftibuten, and is a third-generation cephalosporin with antibacterial activity.
-
DescriptionCeftibuten dihydrate is the dihydrate form of ceftibuten, and is a third-generation cephalosporin with antibacterial activity.(In Vitro):Ceftibuten (Sch-39720) is highly active against Haemophilus influenza, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella sp., and Proteus sp. and moderately active against Serratia sp. and Streptococcus pyogenes. Ceftibuten is relatively inactive against enterococci and staphylococci and is only weakly active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and obligate anaerobes. It is also stable in the presence of most β-lactamase-producing organisms except βBacteroides fragilis. Ceftibuten is very active against strains of the family Enterobacteriaceae (mean MIC for 90% of strains=0.25 μg/ml) but less active against Campylobacterjejuni (mean MIC for 90% of strains=16.0 μg/ml).(In Vivo):Ceftibuten, a biologically stableβ-lactam antibiotic, has been shown to be transported by the small peptide transport system, to have relatively high affinity for the carrier and to show clear stereoselective and proton-gradient dependent transport characteristics in rat intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles.
-
In VitroCeftibuten (Sch-39720) is highly active against Haemophilus influenza, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella sp., and Proteus sp. and moderately active against Serratia sp. and Streptococcus pyogenes. Ceftibuten is relatively inactive against enterococci and staphylococci and is only weakly active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and obligate anaerobes. It is also stable in the presence of most β-lactamase-producing organisms except βBacteroides fragilis. Ceftibuten is very active against strains of the family Enterobacteriaceae (mean MIC for 90% of strains=0.25 μg/ml) but less active against Campylobacterjejuni (mean MIC for 90% of strains=16.0 μg/ml).
-
In VivoCeftibuten, a biologically stableβ-lactam antibiotic, has been shown to be transported by the small peptide transport system, to have relatively high affinity for the carrier and to show clear stereoselective and proton-gradient dependent transport characteristics in rat intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles.
-
SynonymsSch-39720 dihydrate
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorBacterial|Antibiotic
-
Research AreaUrinary system
-
IndicationPyelonephritis
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number118081-34-8
-
Formula Weight446.46
-
Molecular FormulaC15H18N4O8S2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:95 mg/mL (212.78 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESC1C=C(N2C(S1)C(C2=O)NC(=O)C(=CCC(=O)O)C3=CSC(=N3)N)C(=O)O.O.O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. JONES, RONALD N. Ceftibuten: a review of antimicrobial activity, spectrum and other microbiologic features.[J]. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, 1995, 14(14):S77-83.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Fidaxomicin
Fidaxomicin(OPT-80; PAR-101) is a?new class of narrow spectrum macrocyclic antibiotic drug.
-
ClpB-IN-1
ClpB-IN-1 is a potential antimicrobial agent.ClpB-IN-1 is a potent ClpB inhibitor.
-
Ceforanide
Ceforanide is a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic with bactericidal activity. Ceforanide causes inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis by inactivating penicillin binding proteins (PBPs) thereby interfering with the final transpeptidation step required for cross-linking of peptidoglycan units which are a component of the cell wall.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


