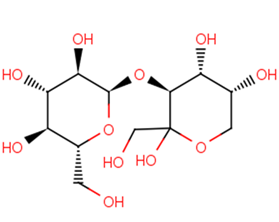
D-(+)-Turanose
CAS No. 547-25-1
D-(+)-Turanose( —— )
Catalog No. M20273 CAS No. 547-25-1
D(+)-Turanose is a naturally occuring compound. It is a reducing disaccharide.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 33 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameD-(+)-Turanose
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionD(+)-Turanose is a naturally occuring compound. It is a reducing disaccharide.
-
DescriptionD(+)-Turanose is a naturally occuring compound. It is a reducing disaccharide.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number547-25-1
-
Formula Weight342.3
-
Molecular FormulaC12H22O11
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O:130 mg/mL (379.78 mM)
-
SMILESOC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@H](O)COC2(O)CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Joo-Yeon C Jihye L Daeyeon L et al. Acute and 13-week subchronic toxicological evaluations of turanose in mice[J]. Nutrition Research and Practice 2017 11(6):452-.
molnova catalog



related products
-
L-Galactose
L-Galactose (Galactose, L-) is a natural product that is widely found in plants and animals. L-Galactose has been shown to be a key intermediate in the molecular pathway for the conversion of D-glucose to oxalic acid in Pistia stratiotes.
-
Leukotriene C4
Leukotriene C4 (LTC4) is an arachidonate lipid mediator that regulates leukocyte recruitment and function at sites of inflammation.
-
3-Methyl-2-oxovaleri...
3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid is an abnormal metabolite that arises from the incomplete breakdown of branched-chain amino acids. 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid is a neurotoxin an acidogen and a metabotoxin. A neurotoxin causes damage to nerve cells and nerve tissues.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


