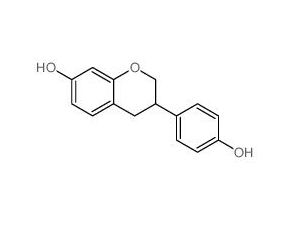
(±)-Equol
CAS No. 94105-90-5
(±)-Equol( —— )
Catalog No. M19273 CAS No. 94105-90-5
Equol is a non-steroidal estrogen produced from the metabolism of the isoflavonoid phytoestrogen daidzen by human intestinal microflora.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 29 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 29 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 56 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 73 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 99 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 130 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name(±)-Equol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionEquol is a non-steroidal estrogen produced from the metabolism of the isoflavonoid phytoestrogen daidzen by human intestinal microflora.
-
DescriptionEquol is a non-steroidal estrogen produced from the metabolism of the isoflavonoid phytoestrogen daidzen by human intestinal microflora. The estrogen receptor (ER) agonist activity of the naturally occurring (S)-enantiomer (EC50 = 85 and 65 nM for human ERα and ERβ, respectively) is similar to that of genistein but exceeds that of daidzein. (S)-Equol preferentially binds ERβ (Ki = 0.73 nM) and demonstrates approximately 9-fold lower affinity for ERα (Ki = 6.41 nM). (S)-equol is also a potent antagonist of dihydrotestosterone, which has important implications for prostate cancer and other androgen-mediated pathologies.(In Vitro):Equol is first isolated and identified from pregnant-mares' urine and later found in the urine of the goat, cow, hen and sheep. Equol, unlike the soy isoflavones daidzein or genistein, has a chiral center and therefore can occur as 2 distinct diastereoisomers. S-equol is the exclusive product of human intestinal bacterial synthesis from soy isoflavones and both enantiomers are bioavailable. S-equol has a high affinity for estrogen receptor beta (Ki=0.73 nM), whereas R-equol is relatively inactive. Equol could promote the proliferation and differentiation of rat osteoblasts through activating the ER-PKCα-related signaling pathway. The alkaline phosphatase activity also increases significantly in all of the equol and 17β-estradiol (E2 ) groups. Equol also significantly elevates the osteocalcin levels.(In Vivo):Equol is a modest natriuretic and vasorelaxant agent in the rat. Orally administered equol is about 8-fold less potent than orally administered furosemide. In isolated aortic rings precontracted by administration of phenylephrine, administration of equol relaxes the contracted aorta. Equol possesses anticancer activity that suppresses tumor formation via apoptosis induction in rats with mammary gland tumors. In addition, equol shows a hepatic protective effect by acting as an antioxidant and by reducing apoptosis.
-
In VitroEquol is first isolated and identified from pregnant-mares' urine and later found in the urine of the goat, cow, hen and sheep. Equol, unlike the soy isoflavones daidzein or genistein, has a chiral center and therefore can occur as 2 distinct diastereoisomers. S-equol is the exclusive product of human intestinal bacterial synthesis from soy isoflavones and both enantiomers are bioavailable. S-equol has a high affinity for estrogen receptor beta (Ki=0.73 nM), whereas R-equol is relatively inactive. Equol could promote the proliferation and differentiation of rat osteoblasts through activating the ER-PKCα-related signaling pathway. The alkaline phosphatase activity also increases significantly in all of the equol and 17β-estradiol (E2 ) groups. Equol also significantly elevates the osteocalcin levels.
-
In VivoEquol is a modest natriuretic and vasorelaxant agent in the rat. Orally administered equol is about 8-fold less potent than orally administered furosemide. In isolated aortic rings precontracted by administration of phenylephrine, administration of equol relaxes the contracted aorta (concentration for half-maximal activity 58.9±16 μM). Equol possesses anticancer activity that suppresses tumor formation via apoptosis induction in rats with mammary gland tumors. In addition, equol shows a hepatic protective effect by acting as an antioxidant and by reducing apoptosis.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorERα| ERβ
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number94105-90-5
-
Formula Weight242.3
-
Molecular FormulaC15H14O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL; 412.76 mM
-
SMILESC1C(COc2c1ccc(c2)O)c1ccc(cc1)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
5-CFDA
5-CFDA(5-Carboxyfluorescein diacetate) is membrane-permeant. It can be loaded into cells via incubation and hydrolyzed by intracellular esterases to 5-carboxyfluorescein that is used for labeling human intervertebral disk cells in vitro for fluorescence microscopy.
-
PAR-3 (1-6) (human)
PAR3 (1-6) is a synthetic peptide agonist of proteinase-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) that corresponds to residues 1-6 of the amino terminal tethered ligand sequence of human PAR3 and residues 39-44 of the full-length human sequence. PAR3 (1-6) activates p42/44 MAPK signaling in fibroblasts expressing PAR1, but not PAR3, an effect that can be blocked by the PAR1 antagonist RWJ 56110.
-
Methoxyamine HCl
Methoxyamine HCl covalently binds to apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) DNA damage sites and inhibits base excision repair (BER), which may result in an increase in DNA strand breaks and apoptosis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


