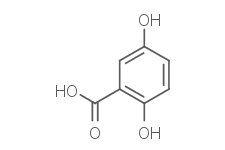
Gentisic acid
CAS No. 490-79-9
Gentisic acid( Gentisic acid | NSC 27224 | NSC-27224 )
Catalog No. M18643 CAS No. 490-79-9
Gentisic acid is a dihydroxybenzoic acid.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 42 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 75 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 114 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameGentisic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionGentisic acid is a dihydroxybenzoic acid.
-
DescriptionGentisic acid is a dihydroxybenzoic acid. It is a derivative of benzoic acid and a minor (1%) product of the metabolic break down of aspirin, excreted by the kidneys. It is also found in the African tree Alchornea cordifolia and in wine.(In Vitro):2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (Gentisic acid) is a derivative of benzoic and a minor product of the metabolic break down of aspirin. 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is also a component of many traditional liquors and herbal remedies, is singled out as a powerful inhibitor of fibroblast growth factors. 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is used as a lead to identify additional compounds with better inhibitory characteristics generating a new chemical class of fibroblast growth factor inhibitors that includes the agent responsible for alkaptonuria. Through low and high resolution approaches, using representative members of the fibroblast growth factor family and their cell receptors, it is shown that this class of inhibitors may employ two different mechanisms to interfere with the assembly of the signaling complexes that trigger fibroblast growth factor-driven mitogenesis.(In Vivo):It is verified from in vivo disease models that this group of inhibitors (e.g., 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid) may be of interest to treat cancer and angiogenesis-dependent diseases.
-
In Vitro2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (Gentisic acid) is a derivative of benzoic and a minor product of the metabolic break down of aspirin. 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is also a component of many traditional liquors and herbal remedies, is singled out as a powerful inhibitor of fibroblast growth factors. 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is used as a lead to identify additional compounds with better inhibitory characteristics generating a new chemical class of fibroblast growth factor inhibitors that includes the agent responsible for alkaptonuria. Through low and high resolution approaches, using representative members of the fibroblast growth factor family and their cell receptors, it is shown that this class of inhibitors may employ two different mechanisms to interfere with the assembly of the signaling complexes that trigger fibroblast growth factor-driven mitogenesis.
-
In VivoIt is verified from in vivo disease models that this group of inhibitors (e.g., 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid) may be of interest to treat cancer and angiogenesis-dependent diseases.
-
SynonymsGentisic acid | NSC 27224 | NSC-27224
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number490-79-9
-
Formula Weight154.12
-
Molecular FormulaC7H6O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL; 648.85 mM
-
SMILESc1cc(c(cc1O)C(=O)O)O
-
Chemical NameBenzoic acid, 2,5-dihydroxy-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Wang L, et al. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 Oct 15;937:91-6.
molnova catalog



related products
-
G-418 disulfate
An aminoglycoside antibiotic similar in structure to gentamicin B1; blocks polypeptide synthesis by inhibiting the elongation step in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
-
WAY-658650
WAY-658650 has antibacterial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
-
ANT3310
ANT3310 is an inhibitor of broad-spectrum covalent Serine β-Lactamase with IC50s ranging from 1 nM to 175 nM for AmpC, CTX-M-15, TEM-1, OXA-48, OXA-23, and KPC-2. ANT3310 can be used in studies about bacterial infection.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


