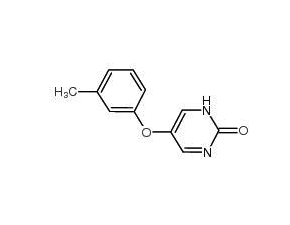
Tolimidone
CAS No. 41964-07-2
Tolimidone( MLR-1003 | MLR 1003 | MLR1003 | CID-39065 )
Catalog No. M18535 CAS No. 41964-07-2
MLR-1023 is a chemical compound which inhibits acid secretion in animal models and also acts as a bronchodilator in histamine-challenged animals.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 46 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 67 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 113 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 177 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 265 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameTolimidone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMLR-1023 is a chemical compound which inhibits acid secretion in animal models and also acts as a bronchodilator in histamine-challenged animals.
-
DescriptionMLR-1003 is a Lyn kinase activator that induces glycemic control.(In Vitro):Incubation of Tolimidone (MLR-1023) with Lyn kinase elicits a repeatable 50% increase in enzyme activity. Tolimidone elicits a concentration-dependent increase in Lyn kinase activation with a 2.3- and 2.1-fold increase achieved at concentrations of 3 and 10 μM, respectively. Inclusion of Tolimidone (100 μM) increases Lyn kinase activity by 3-fold at each ATP concentration tested (Vmax=2601 U/mg). Tolimidone-mediated activation of Lyn kinase increases in proportion to the length of preincubation period in the absence of ATP.(In Vivo):Administration of Tolimidone (MLR-1023) (30 mg/kg i.p.) significantly (p<0.05) lowers blood glucose levels to 148 and 158 mg/dL, 30 and 90 min after administration, respectively. Tolimidone significantly increases adipocyte differentiation and adiponectin production by 3.7- and 19-fold, respectively. Tolimidone elicits a dose-dependent potentiation of the insulin response, with a maximal effect observed with a dose level of 30 mg/kg.
-
In VitroIncubation of Tolimidone (MLR-1023) with Lyn kinase elicits a repeatable 50% increase in enzyme activity. Tolimidone elicits a concentration-dependent increase in Lyn kinase activation with a 2.3- and 2.1-fold increase achieved at concentrations of 3 and 10 μM, respectively. Inclusion of Tolimidone (100 μM) increases Lyn kinase activity by 3-fold at each ATP concentration tested (Vmax=2601 U/mg). Tolimidone-mediated activation of Lyn kinase increases in proportion to the length of preincubation period in the absence of ATP.
-
In VivoAdministration of Tolimidone (MLR-1023) (30 mg/kg i.p.) significantly (p<0.05) lowers blood glucose levels to 148 and 158 mg/dL, 30 and 90 min after administration, respectively. Tolimidone significantly increases adipocyte differentiation and adiponectin production by 3.7- and 19-fold, respectively. Tolimidone elicits a dose-dependent potentiation of the insulin response, with a maximal effect observed with a dose level of 30 mg/kg.
-
SynonymsMLR-1003 | MLR 1003 | MLR1003 | CID-39065
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorLyn kinase
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number41964-07-2
-
Formula Weight202.21
-
Molecular FormulaC11H10N2O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : 150 mg/mL 741.80 mM
-
SMILESCC1=CC=CC(OC2=CNC(=O)N=C2)=C1
-
Chemical Name5-(3-Methylphenoxy)-2(1H)-pyrimidinone
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
α-Synuclein (34-45) ...
α-Synuclein (34-45) (human) is the 34-45 fragment of α-Synuclein. α-Synuclein is an abundant neuronal protein that is highly abundant in presynaptic nerve terminals. α-Synuclein is a Parkinson's disease (PD) biomarker.
-
Aesculitannin B
Aesculitannin B
-
Anisindione
Anisindione is a synthetic anticoagulant and an indanedione derivative.?It prevents the formation of active procoagulation factors II, VII, IX, and X, as well as the anticoagulant proteins C and S, in the liver by inhibiting the vitamin K–mediated gamma-carboxylation of precursor proteins.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


