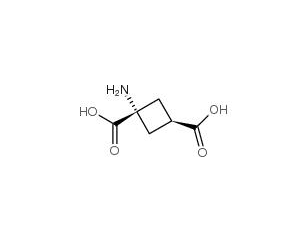
Cis-ACBD
CAS No. 73550-55-7
Cis-ACBD( cis-ABCD )
Catalog No. M17584 CAS No. 73550-55-7
2, 4-methanoglutamate is a potent and selective N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor agonist.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 94 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 157 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 341 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 495 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 704 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCis-ACBD
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2, 4-methanoglutamate is a potent and selective N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor agonist.
-
Descriptioncis-ABCD is a potent, competitive and selective inhibitor of glutamate uptake.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonymscis-ABCD
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetSyk
-
Recptoraspartate
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number73550-55-7
-
Formula Weight159.14
-
Molecular FormulaC6H9NO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES[C@]1(C[C@@H](C1)C(=O)O)(C(=O)O)N
-
Chemical Namecis-1-Aminocyclobutane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Thomas HL, et al. cis-2,4-methanoglutamate is a potent and selective N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor agonist. 1990, 182(3):397-404.
molnova catalog



related products
-
MNS
MNS is a tyrosine kinases inhibitor inhibits Syk Src p97 with IC50 of 2.5 μM 29.3 μM and 1.7 μM respectively.
-
Cevidoplenib dimesyl...
Cevidoplenib dimesylate hydrochloride is a spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor showing potential immunomodulating and anti-inflammatory properties.
-
TAK-659 hydrochlorid...
TAK-659 hydrochloride (Mivavotinib, TAK659) is a potent, selective and orally available SYK inhibitor with IC50 of 3.2 nM.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


