R-IMPP
CAS No. 2133832-83-2
R-IMPP( —— )
Catalog No. M17432 CAS No. 2133832-83-2
R-IMPP is an inhibitor of PCSK9 translation. R-IMPP stimulates uptake of LDL-C in hepatoma cells by increasing LDL-R levels, without altering levels of secreted transferrin.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 49 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 77 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 135 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 281 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 500 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 718 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameR-IMPP
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionR-IMPP is an inhibitor of PCSK9 translation. R-IMPP stimulates uptake of LDL-C in hepatoma cells by increasing LDL-R levels, without altering levels of secreted transferrin.
-
DescriptionR-IMPP is an inhibitor of PCSK9 translation. R-IMPP stimulates uptake of LDL-C in hepatoma cells by increasing LDL-R levels, without altering levels of secreted transferrin.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorPCSK9
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2133832-83-2
-
Formula Weight389.21
-
Molecular FormulaC24H27N3O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 41 mg/mL; 105.27 mM
-
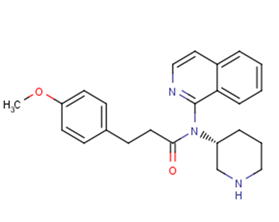
SMILESCOC1=CC=C(CCC(N(C2=C(C=CC=C3)C3=CC=N2)[C@H]4CNCCC4)=O)C=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
cystine
Not considered one of the 20 amino acids, Cystine is a sulfur-containing derivative obtained from oxidation of cysteine amino acid thiol side chains.
-
Fibrinogen-Binding P...
Fibrinogen-Binding Peptide (designed by anticomplementarity hypothesis) is a presumptive peptide mimic of the vitronectin binding site on the fibrinogen receptor. Fibrinogen, a soluble plasma protein, is a cofactor in platelet activation. It is converted to fibrin in a reaction catalyzed by thrombin.
-
Ninerafaxstat
Ninerafaxstat hifts cellular metabolism from fatty acid oxidation to glucose oxidation.Ninerafaxstat decreases fatty acid oxidation and improve overall mitochondrial respiration.Ninerafaxstat inhibit the growth and proliferation of cancer cells .



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


