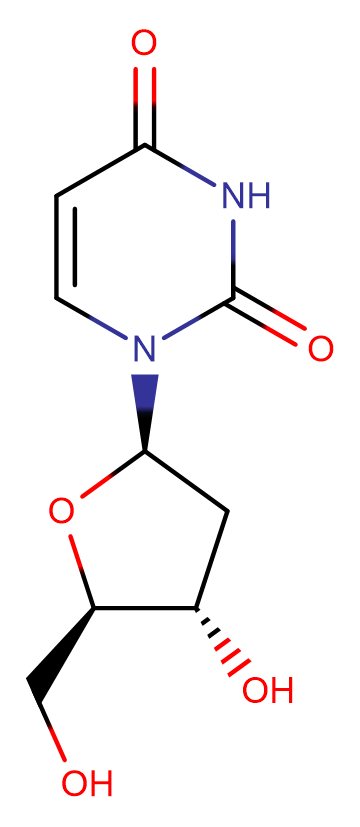
2'-Deoxyuridine
CAS No. 951-78-0
2'-Deoxyuridine( —— )
Catalog No. M16806 CAS No. 951-78-0
2'-Deoxyuridine. An antimetabolite that is converted to deoxyuridine triphosphate during DNA synthesis.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 42 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 60 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 83 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2'-Deoxyuridine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2'-Deoxyuridine. An antimetabolite that is converted to deoxyuridine triphosphate during DNA synthesis.
-
Description2'-Deoxyuridine. An antimetabolite that is converted to deoxyuridine triphosphate during DNA synthesis. Laboratory suppression of deoxyuridine is used to diagnose megaloblastic anemias due to vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetDNA/RNA Synthesis
-
RecptorThymidylate synthase| Upp
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number951-78-0
-
Formula Weight228.2
-
Molecular FormulaC9H12N2O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityLimited solubility
-
SMILESC1[C@@H]([C@H](O[C@H]1N2C=CC(=O)NC2=O)CO)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Honeywell RJ, et al. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Mar;60:73-8
molnova catalog



related products
-
Holomycin
Holomycin (N-Demethylthiolutin) is a secondary metabolite of dithiopyrrolidone. HolomycinHolomycin, an antibiotic secondary metabolite, is required for the biofilm formation of natural photogenic Bacillus galatheae S2753 and is also a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
-
RI-1
RI-1 is a RAD51 inhibitor with IC50 ranging from 5 to 30μM.
-
1-Hydroxyanthraquino...
1-Hydroxyanthraquinone is an anthraquinone that has been found in Morinda officinalis and has genotoxic and carcinogenic activities. 1-Hydroxyanthraquinone generates strong DNA repair response.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


