Seladelpar
CAS No. 851528-79-5
Seladelpar( MBX 8025 | RWJ 800025 | MBX8025 | RWJ800025 )
Catalog No. M16187 CAS No. 851528-79-5
A potent, selective, orally bioavailable PPARδ agonist for the treatment of dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 46 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 69 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 130 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 221 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 331 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 456 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSeladelpar
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA potent, selective, orally bioavailable PPARδ agonist for the treatment of dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
-
DescriptionA potent, selective, orally bioavailable PPARδ agonist for the treatment of dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).Dyslipidemia Phase 2 Clinical(In Vitro):MBX-8025 is an orally active, potent (EC50=2 nM), and specific (750-fold and 2500-fold compared with PPARα or PPARγ receptors, respectively) PPARδ agonist being developed as a lipid-altering agent.(In Vivo):In atherogenic diet-fed Wt mice, administration of Seladelpar sodium salt reduces body weight by ~18% (P<0.05). In contrast, Seladelpar sodium salt produces minimal effect on body weight in atherogenic diet-fed foz/foz mice. Seladelpar sodium salt lowers serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels in foz/foz mice (P<0.05) and similarly (but not significantly) in Wt mice. Seladelpar sodium salt normalizes serum cholesterol and decreases triglycerides in both genotypes (P<0.05). Seladelpar sodium salt abolishes hepatocyte ballooning (P<0.05) and decreases the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score by ~50%. Seladelpar sodium salt also significantly reduces sirius red-positive areas in foz/foz mice (P<0.05).
-
In VitroSeladelpar (MBX-8025) is an orally active, potent (2 nM), and specific (>750-fold and >2500-fold compared with PPAR-α or PPAR-γ receptors, respectively) PPAR-δ agonist being developed as a lipid-altering agent. Seladelpar is a potent, and selective PPAR-δ agonist (50% effect concentration human PPAR-δ=2 nM, PPAR-α=1,600 nM) that demonstrates favorable effects on insulin resistance, diabetes, and atherogenic dyslipidemia.
-
In VivoFrom weaning, female Alms1 mutant (foz/foz) mice and wild-type littermates are fed an atherogenic diet for 16 weeks; groups (n=8-12) are then randomized to receive Seladelpar (10 mg/kg) or vehicle (1% methylcellulose) by gavage for 8 weeks. Despite minimally altering body weight, Seladelpar normalizes hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and glucose disposal in foz/foz mice. Serum alanine aminotransferase ranges 300-600 U/L in vehicle-treated foz/foz mice; Seladelpar reduces alanine aminotransferase by 50%. In addition, Seladelpar normalizes serum lipids and hepatic levels of free cholesterol and other lipotoxic lipids that are increased in vehicle-treated foz/foz versus wild-type mice. This abolished hepatocyte ballooning and apoptosis, substantially reduce steatosis and liver inflammation, and improve liver fibrosis. In vehicle-treated foz/foz mice, the mean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score is 6.9, indicating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH); Seladelpar reverses NASH in all foz/foz mice (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score 3.13). In atherogenic diet-fed Wt mice, administration of Seladelpar reduces body weight by ~18% (P<0.05). In contrast, Seladelpar produces minimal effect on body weight in atherogenic diet–fed foz/foz mice. These animals develope severe hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and whole-body insulin resistance after 16 weeks (P<0.05); Seladelpar strikingly improves these indices (P<0.05). After intraperitoneal glucose injection, blood glucose reaches ~32 mM in vehicle-treated versus ~14 mM in Seladelpar-treated foz/foz mice (P<0.05); the area under the blood glucose disappearance curve is correspondingly lower in Seladelpar-treated foz/foz mice (P<0.05). Seladelpar produces a proportionally similar effect on glucose handling in atherogenic diet–fed Wt mice (P<0.05).
-
SynonymsMBX 8025 | RWJ 800025 | MBX8025 | RWJ800025
-
PathwayMetabolic Enzyme/Protease
-
TargetPPAR
-
RecptorPPARα|PPAR-δ
-
Research AreaCardiovascular Disease
-
IndicationDyslipidemia
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number851528-79-5
-
Formula Weight444.465
-
Molecular FormulaC21H23F3O5S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM ( < 1 mg/ml refers to the product slightly soluble or insoluble )
-
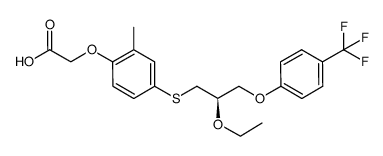
SMILESCCOC(COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(F)(F)F)CSC2=CC(=C(C=C2)OCC(=O)O)C
-
Chemical Name(R)-2-(4-((2-ethoxy-3-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)propyl)thio)-2-methylphenoxy)acetic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Bays HE, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Sep;96(9):2889-97.
2. Jones D, et al. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Oct;2(10):716-726.
3. Choi YJ, et al. Atherosclerosis. 2012 Feb;220(2):470-6.
molnova catalog



related products
-
BADGE
Bisphenol a diglycidyl ether is a Standardized Chemical Allergen. The physiologic effect of bisphenol a diglycidyl ether is by means of Increased Histamine Release, and Cell-mediated Immunity.
-
Benzo[b]thiophene-7-...
Benzo[b]thiophene-7-propanoic acid, α-methoxy-4-[2-(5-methyl-2-phenyl-4-oxazolyl)ethoxy]-, (αR)- is a dual PPARα/γ agonist with EC50 of 0.358μM and 1.21μM.
-
CGS 15435
CGS 15435 is a potent thromboxen (TxA2) synthetase inhibitor (IC50: 1 nM). CGS 15435 acts on PGI2 synthase, cyclooxygenase and liposynthase with much less selectivity than on thromboxin synthase.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


