Bitopertin
CAS No. 845614-11-1
Bitopertin( RG1678 | RO4917838 | RG-1678 | RG 1678 | RO-4917838 | RO 4917838 )
Catalog No. M16141 CAS No. 845614-11-1
A potent and selective GlyT1 inhibitor with EC50 of 30 nM; no activity for GlyT2, hERG, CYP450 enzymes above 10 uM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 65 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 88 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 203 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 372 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 554 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBitopertin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA potent and selective GlyT1 inhibitor with EC50 of 30 nM; no activity for GlyT2, hERG, CYP450 enzymes above 10 uM.
-
DescriptionA potent and selective GlyT1 inhibitor with EC50 of 30 nM; no activity for GlyT2, hERG, CYP450 enzymes above 10 uM; shows brain penetratione and excellent pharmacokinetic in vivo.Schizophrenia Phase 3 Clinical(In Vitro):Bitopertin (RG1678) competitively blocks [3H]ORG24598 binding sites at human GlyT1b in membranes from Chinese hamster ovary cells. Bitopertin potently inhibits [3H]glycine uptake in cells stably expressing hGlyT1b and mGlyT1b, with IC50 values of 25±2 nM and 22±5 nM, respectively (n=6). Conversely, Bitopertin has no effect on hGlyT2-mediated glycine uptake up to 30 μM concentration. Bitopertin has high affinity for the recombinant hGlyT1b transporter. Under equilibrium conditions (1 h at room temperature), Bitopertin displaces [3H]ORG24598 binding with a Ki of 8.1 nM. In hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells, Bitopertin enhances NMDA-dependent long-term potentiation at 100 nM but not at 300 nM. Additional profiling revealed that Bitopertin (RG1678) has an excellent selectivity profile against the GlyT2 isoform (IC50>30 μM) and toward a panel of 86 targets including transmembrane and soluble receptors, enzymes, ion channels, and monoamine transporters (<41% inhibition at 10 μM is measured for all targets). (In Vivo):Bitopertin (RG1678) dose-dependently increases cerebrospinal fluid and striatal levels of glycine measured bymicrodialysis in rats. Additionally Bitopertin attenuates hyperlocomotion induced by the psychostimulant D-amphetamine or the NMDA receptor glycine site antagonist L-687,414 in mice. Bitopertin also prevents the hyper-response to D-amphetamine challenge in rats treated chronically with phencyclidine, an NMDA receptor open-channel blocker. Administration of vehicle has no effect on extracellular levels of striatal glycine, which remained constant throughout the experiment. In contrast, p.o. administration of Bitopertin (1-30 mg/kg) produced a dose-dependent increase in extracellular glycine levels. Bitopertin 30 mg/kg produces glycine levels 2.5 times higher than pretreatment levels. A similar dose-dependent increase in glycine concentration is observed in the CSF of rats treated p.o. with Bitopertin (1-10 mg/kg) compared with vehicle-treated animals, 3 h after drug administration. Interestingly, the level of CSF glycine increase 3 h after Bitopertin dosing is very similar to the increase in the microdialysis experiment at the same time point. In vivo pharmacokinetic studies in rat and monkey reveals that Bitopertin (RG1678) has, in both species, a low plasma clearance, an intermediate volume of distribution, a good oral bioavailability (78% for rat, 56% for monkey), and a favorable terminal half-life (5.8 h for rat, 6.4 h for monkey). The plasma protein binding is high in the two preclinical species (97%) and in human (98%). The CNS penetration of Bitopertin in rat (brain/plasma=0.7) is better than that in mouse (brain/plasma=0.5).
-
In VitroBitopertin (RG1678) competitively blocks [3H]ORG24598 binding sites at human GlyT1b in membranes from Chinese hamster ovary cells. Bitopertin potently inhibits [3H]glycine uptake in cells stably expressing hGlyT1b and mGlyT1b, with IC50 values of 25±2 nM and 22±5 nM, respectively (n=6). Conversely, Bitopertin has no effect on hGlyT2-mediated glycine uptake up to 30 μM concentration. Bitopertin has high affinity for the recombinant hGlyT1b transporter. Under equilibrium conditions (1 h at room temperature), Bitopertin displaces [3H]ORG24598 binding with a Ki of 8.1 nM. In hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells, Bitopertin enhances NMDA-dependent long-term potentiation at 100 nM but not at 300 nM. Additional profiling revealed that Bitopertin (RG1678) has an excellent selectivity profile against the GlyT2 isoform (IC50>30 μM) and toward a panel of 86 targets including transmembrane and soluble receptors, enzymes, ion channels, and monoamine transporters (<41% inhibition at 10 μM is measured for all targets).
-
In VivoBitopertin (RG1678) dose-dependently increases cerebrospinal fluid and striatal levels of glycine measured bymicrodialysis in rats. Additionally Bitopertin attenuates hyperlocomotion induced by the psychostimulant D-amphetamine or the NMDA receptor glycine site antagonist L-687,414 in mice. Bitopertin also prevents the hyper-response to D-amphetamine challenge in rats treated chronically with phencyclidine, an NMDA receptor open-channel blocker. Administration of vehicle has no effect on extracellular levels of striatal glycine, which remained constant throughout the experiment. In contrast, p.o. administration of Bitopertin (1-30 mg/kg) produced a dose-dependent increase in extracellular glycine levels. Bitopertin 30 mg/kg produces glycine levels 2.5 times higher than pretreatment levels. A similar dose-dependent increase in glycine concentration is observed in the CSF of rats treated p.o. with Bitopertin (1-10 mg/kg) compared with vehicle-treated animals, 3 h after drug administration. Interestingly, the level of CSF glycine increase 3 h after Bitopertin dosing is very similar to the increase in the microdialysis experiment at the same time point. In vivo pharmacokinetic studies in rat and monkey reveals that Bitopertin (RG1678) has, in both species, a low plasma clearance, an intermediate volume of distribution, a good oral bioavailability (78% for rat, 56% for monkey), and a favorable terminal half-life (5.8 h for rat, 6.4 h for monkey). The plasma protein binding is high in the two preclinical species (97%) and in human (98%). The CNS penetration of Bitopertin in rat (brain/plasma=0.7) is better than that in mouse (brain/plasma=0.5).
-
SynonymsRG1678 | RO4917838 | RG-1678 | RG 1678 | RO-4917838 | RO 4917838
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetGlyT
-
RecptorGlyT1
-
Research AreaNeurological Disease
-
IndicationSchizophrenia
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number845614-11-1
-
Formula Weight543.455
-
Molecular FormulaC21H20F7N3O4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility10 mM in DMSO
-
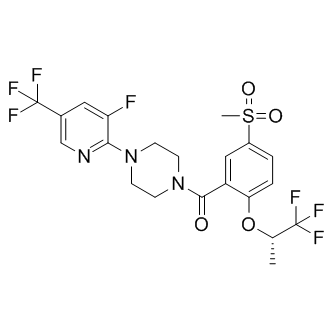
SMILESFC1=C(N2CCN(C(C3=C(O[C@H](C(F)(F)F)C)C=CC(S(C)(=O)=O)=C3)=O)CC2)N=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1
-
Chemical NameMethanone, [4-[3-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]-1-piperazinyl][5-(methylsulfonyl)-2-[(1S)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-methylethoxy]phenyl]-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Pinard E, et al. J Med Chem. 2010 Jun 24;53(12):4603-14.
2. Alberati D, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2012 Feb;62(2):1152-613. Martin-Facklam M, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Feb;38(3):504-12.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Org 25543 hydrochlor...
Org 25543 hydrochloride is a potent and selective glycine transporter type 2 (GlyT2) inhibitor (IC50 = 16 nM for hGlyT2). Displays no activity at GlyT1 or 56 other common biological targets (≥ 100 μM), in a glycine uptake assay in CHO cells.
-
Opiranserin
Opiranserin (VVZ-149, VVZ-000149) is a?potent, selective, mixed glycine GlyT2 transporter blocker (IC50= 0.86 uM).
-
AMG 747
A nanomolar potent, selective, and orally bioavailable glycine transporter type-1 (GlyT1) inhibitor for the treatment of negative symptoms associated with schizophrenia.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


