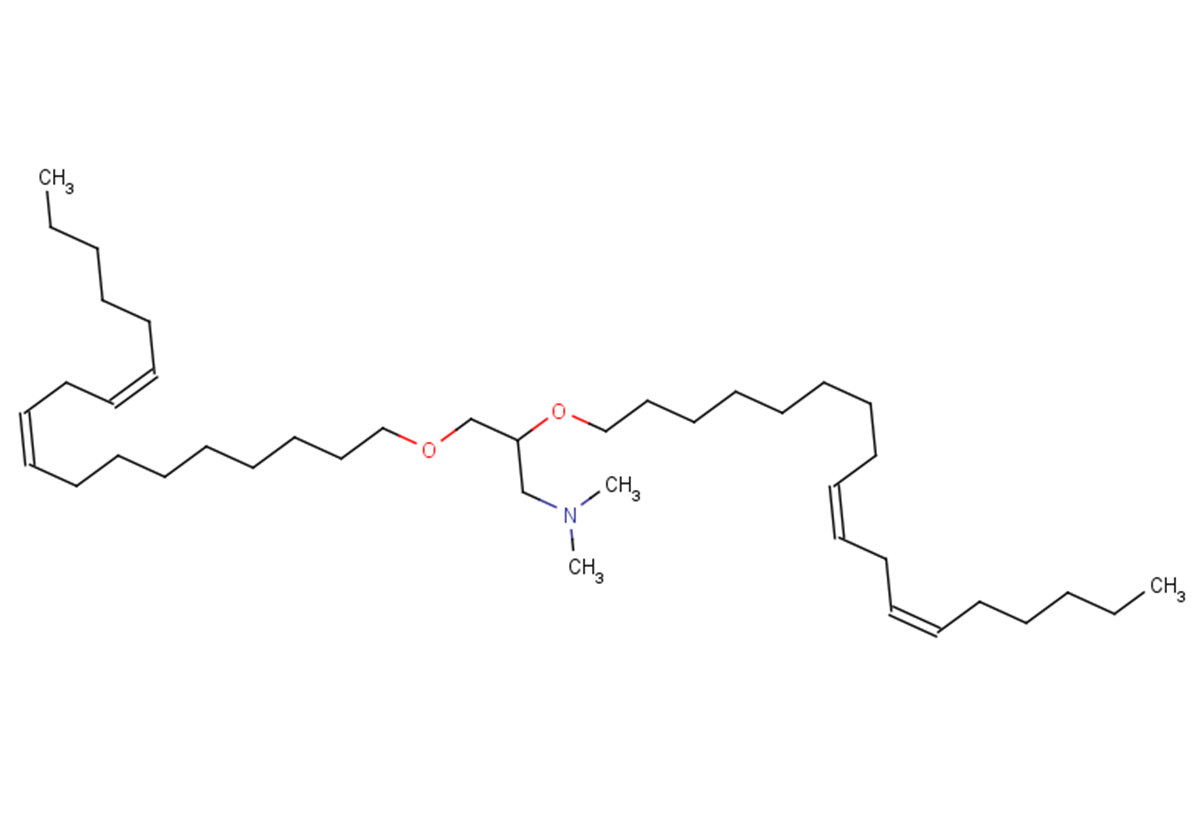
DLinDMA
CAS No. 871258-12-7
DLinDMA( —— )
Catalog No. M24885 CAS No. 871258-12-7
DLinDMA, as a benchmark, is a key stable nucleic acid lipid particleslipid component.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 53 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 77 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 114 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 172 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDLinDMA
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDLinDMA, as a benchmark, is a key stable nucleic acid lipid particleslipid component.
-
DescriptionDLinDMA, as a benchmark, is a key stable nucleic acid lipid particleslipid component.
-
In VitroThe structure of DLinDMA can be divided into three main regions: the hydrocarbon chains, the linker and the headgroup.
-
In VivoDLinDMA has virtually indistinguishable blood pharmacokinetic profiles in mice.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number871258-12-7
-
Formula Weight616.06
-
Molecular FormulaC41H77NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol: 100 mg/mL (162.32 mM);DMSO: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble)
-
SMILESCCCCC/C=C\C/C=C\CCCCCCCCOCC(OCCCCCCCC/C=C\C/C=C\CCCCC)CN(C)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Semple SC, et al. Rational design of cationic lipids for siRNA delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 2010 Feb;28(2):172-6.
molnova catalog



related products
-
4-Methylumbelliferyl...
4-Methylumbelliferyl-β-D-Glucopyranoside is used in the GCase activity assay based on the catalytic hydrolysis of 4-methylumbelliferyl β-D-glucopyranoside that releases the highly fluorescent 4-methylumbelliferyl (4-MU).
-
MFI8
MFI8 is a compound that regulates mitochondrial fission and can be used to study aging.
-
3-Chloropropiophenon...
3-Chloropropiophenone is a small molecular compound.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


