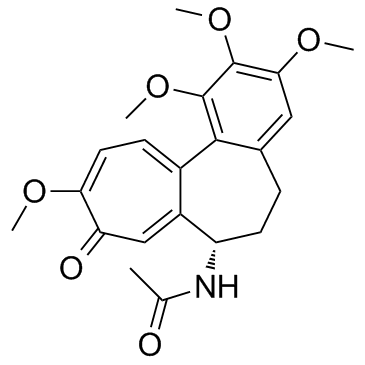
Colchicine
CAS No. 64-86-8
Colchicine( Colchicina | Colchicin | Condylon | Colsaloid | Colchicinum )
Catalog No. M15460 CAS No. 64-86-8
Colchicine is a tubulin inhibitor, it blocks polymerization of microtubules by binding to tubulin (IC50 = 3.2 μM).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 31 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 58 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameColchicine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionColchicine is a tubulin inhibitor, it blocks polymerization of microtubules by binding to tubulin (IC50 = 3.2 μM).
-
DescriptionColchicine is a tubulin inhibitor, it blocks polymerization of microtubules by binding to tubulin (IC50 = 3.2 μM).(In Vitro):Exposure to 1μM Colchicine, a microtubule disrupting agent, triggered apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule cells (CGC). Colchicine treatment also causes alterations in Ca2+ responses to chemical depolarization and a moderate, but progressive, increase in the resting intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Colchicine exerts its biological effects through binding to the soluble tubulin heterodimer, the major component of the microtubule. The Colchicine binding abilities of tubulins from a variety of sources are summarized, and the mechanism of Colchicine binding to brain tubulin is explored in depth. The relationship between colchicinoid structure and tubulin binding activity provides insight into the structural features of Colchicine responsible for high affinity binding to tubulin and is reviewed for analogs in the Colchicine series. The thermodynamic and kinetic aspects of the association are described and evaluated in terms of the binding mechanism. Colchicine binding to tubulin results in unusual alterations in the low energy electronic spectra of Colchicine. The spectroscopic features of Colchicine bound to tubulin are discussed in terms of the nature of the Colchicine-tubulin complex. Attempts to locate the high affinity Colchicine binding site on tubulin are presented. Colchicine treatment inhibits indomethacin-induced small intestinal injury by 86% (1 mg/kg) and 94% (3 mg/kg) as indicated by the lesion index 24 h after indomethacin administration. Colchicine inhibits the protein expression of cleaved caspase-1 and mature IL-1β, without affecting the mRNA expression of NLRP3 and IL-1β. (In Vivo):Vehicle or Colchicine (1 mg/kg) is administered orally 30 min prior to indomethacin administration. The lesions stained with Evans blue in the small intestine are smaller in Colchicine-treated mice than those in vehicle-treated mice 24 h after indomethacin administration. In addition, histological examination shows that Colchicine-treated mice have less mucosal inflammation and ulceration and a decrease in the size and numbers of lesions compared with vehicle-treated mice. Colchicine treatment significantly reduces the lesion index at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg (by 86% and 94%, respectively) compared with vehicle treatment. Colchicine treatment significantly inhibits the protein levels of mature IL-1β at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg (by 56% and 69%, respectively) without affecting those of pro-IL-1β. Colchicine treatment also significantly inhibits the protein levels of cleaved caspase-1 at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg (by 26% and 39%, respectively) without affecting those of pro-caspase-1.
-
In VitroExposure to 1μM Colchicine, a microtubule disrupting agent, triggered apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule cells (CGC). Colchicine treatment also causes alterations in Ca2+ responses to chemical depolarization and a moderate, but progressive, increase in the resting intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Colchicine exerts its biological effects through binding to the soluble tubulin heterodimer, the major component of the microtubule. The Colchicine binding abilities of tubulins from a variety of sources are summarized, and the mechanism of Colchicine binding to brain tubulin is explored in depth. The relationship between colchicinoid structure and tubulin binding activity provides insight into the structural features of Colchicine responsible for high affinity binding to tubulin and is reviewed for analogs in the Colchicine series. The thermodynamic and kinetic aspects of the association are described and evaluated in terms of the binding mechanism. Colchicine binding to tubulin results in unusual alterations in the low energy electronic spectra of Colchicine. The spectroscopic features of Colchicine bound to tubulin are discussed in terms of the nature of the Colchicine-tubulin complex. Attempts to locate the high affinity Colchicine binding site on tubulin are presented. Colchicine treatment inhibits indomethacin-induced small intestinal injury by 86% (1 mg/kg) and 94% (3 mg/kg) as indicated by the lesion index 24 h after indomethacin administration. Colchicine inhibits the protein expression of cleaved caspase-1 and mature IL-1β, without affecting the mRNA expression of NLRP3 and IL-1β.
-
In VivoVehicle or Colchicine (1 mg/kg) is administered orally 30 min prior to indomethacin administration. The lesions stained with Evans blue in the small intestine are smaller in Colchicine-treated mice than those in vehicle-treated mice 24 h after indomethacin administration. In addition, histological examination shows that Colchicine-treated mice have less mucosal inflammation and ulceration and a decrease in the size and numbers of lesions compared with vehicle-treated mice. Colchicine treatment significantly reduces the lesion index at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg (by 86% and 94%, respectively) compared with vehicle treatment. Colchicine treatment significantly inhibits the protein levels of mature IL-1β at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg (by 56% and 69%, respectively) without affecting those of pro-IL-1β. Colchicine treatment also significantly inhibits the protein levels of cleaved caspase-1 at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg (by 26% and 39%, respectively) without affecting those of pro-caspase-1.
-
SynonymsColchicina | Colchicin | Condylon | Colsaloid | Colchicinum
-
PathwayCytoskeleton/Cell Adhesion Molecules
-
TargetMicrotubule/Tubulin
-
Recptormicrotubule
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number64-86-8
-
Formula Weight399.44
-
Molecular FormulaC22H25NO6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubilitysoluble in Water
-
SMILESCC(=O)N[C@H]1CCC2=CC(=C(C(=C2C3=CC=C(C(=O)C=C13)OC)OC)OC)OC
-
Chemical NameN-[(7S)-1,2,3,10-tetramethoxy-9-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-benzo[a]heptalen-7-yl]acetamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Yee KW, et al. Clin Y Res. 2005 Sep 15;11(18):6615-24.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Lys-SMCC-DM1
DM1 is a tubulin inhibitor.?Lys-SMCC-DM1 is the active metabolite of DM1.?
-
Lexibulin dihydrochl...
An orally active tubulin polymerization inhibitor with potent cytotoxic and vascular disrupting activity in vitro and in vivo.
-
Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel is a novel antineoplastic agent, which was discovered in a screen of extracts of thousands of plants and natural products for antineoplastic activity by a National Y Institute program.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


