CEF3
CAS No. 199727-62-3
CEF3( —— )
Catalog No. M30480 CAS No. 199727-62-3
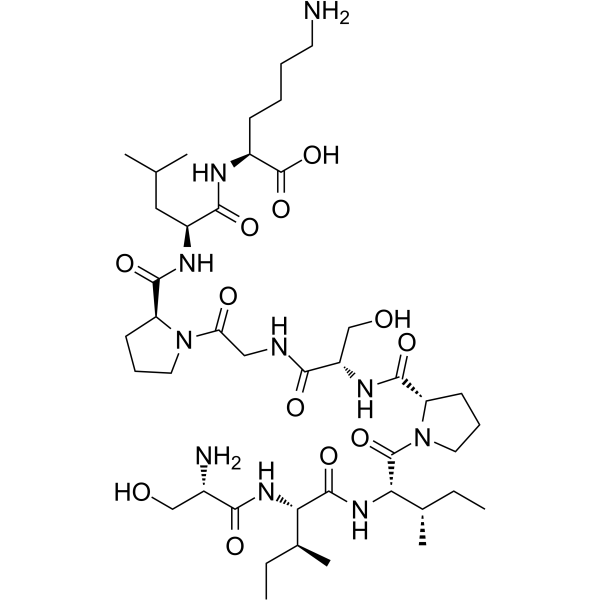
CEF3 (SIIPSGPLK) corresponds to aa 13-21 of the influenza A virus M1 protein. The matrix (M1) protein of influenza A virus is a multifunctional protein that plays essential structural and functional roles in the virus life cycle.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 425 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 721 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCEF3
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCEF3 (SIIPSGPLK) corresponds to aa 13-21 of the influenza A virus M1 protein. The matrix (M1) protein of influenza A virus is a multifunctional protein that plays essential structural and functional roles in the virus life cycle.
-
DescriptionCEF3 (SIIPSGPLK) corresponds to aa 13-21 of the influenza A virus M1 protein. The matrix (M1) protein of influenza A virus is a multifunctional protein that plays essential structural and functional roles in the virus life cycle.(In Vitro):The matrix (M1) protein of influenza A virus is a multifunctional protein that plays essential structural and functional roles in the virus life cycle. It drives virus budding and is the major protein component of the virion, where it forms an intermediate layer between the viral envelope and integral membrane proteins and the genomic ribonucleoproteins (RNPs). It also helps to control the intracellular trafficking of RNPs. These roles are mediated primarily via protein-protein interactions with viral and possibly cellular proteins. The influenza virus M1 is required to induce vRNP nuclear export but that cellular phosphorylation is an additional factor. The influenza virus M1 protein is fundamental to a late event in the virus life cycle-the transfer of vRNPs from the nucleus to the cytosol.
-
In VitroThe matrix (M1) protein of influenza A virus is a multifunctional protein that plays essential structural and functional roles in the virus life cycle. It drives virus budding and is the major protein component of the virion, where it forms an intermediate layer between the viral envelope and integral membrane proteins and the genomic ribonucleoproteins (RNPs). It also helps to control the intracellular trafficking of RNPs. These roles are mediated primarily via protein-protein interactions with viral and possibly cellular proteins. The influenza virus M1 is required to induce vRNP nuclear export but that cellular phosphorylation is an additional factor. The influenza virus M1 protein is fundamental to a late event in the virus life cycle-the transfer of vRNPs from the nucleus to the cytosol.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMicrobiology/Virology
-
TargetInfluenza Virus
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number199727-62-3
-
Formula Weight911.1
-
Molecular FormulaC42H74N10O12
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical NameSequence:Ser-Ile-Ile-Pro-Ser-Gly-Pro-Leu-Lys
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
Noton SL, et al. Identification of the domains of the influenza A virus M1 matrix protein required for NP binding, oligomerization and incorporation into virions. J Gen Virol. 2007 Aug;88(Pt 8):2280-90.
molnova catalog



related products
-
JNJ4796
JNJ4796 (JNJ 4796, JNJ-4796) is an orally active small-molecule fusion inhibitor of influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) with EC50 of 33 nM (H1N1 neutralization).
-
T-1105
T-1105 is a broad-spectrum antiviral inhibitor that demonstrates good activity for various RNA viruses.
-
Glabrone
Glabrone shows antiviral activity against influenza virus.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


