 Home -
Products -
Proteasome/Ubiquitin -
Endogenous Metabolite -
11(Z),14(Z),17(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid
Home -
Products -
Proteasome/Ubiquitin -
Endogenous Metabolite -
11(Z),14(Z),17(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid
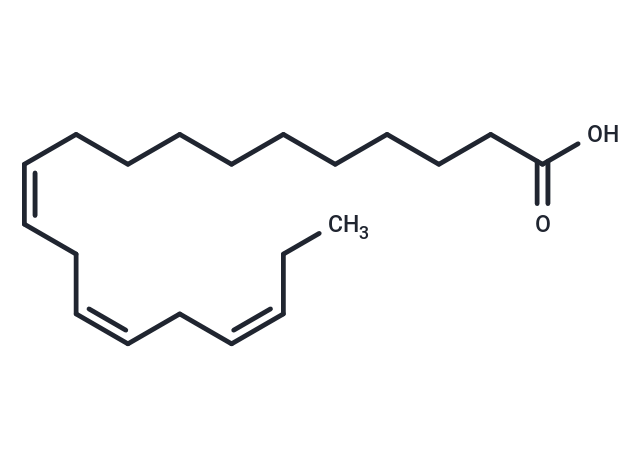
11(Z),14(Z),17(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid
CAS No. 17046-59-2
11(Z),14(Z),17(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M37541 CAS No. 17046-59-2
11(Z),14(Z),17(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid capable of maintaining continuous replication of functional mitochondria in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (KD115).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name11(Z),14(Z),17(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description11(Z),14(Z),17(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid capable of maintaining continuous replication of functional mitochondria in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (KD115).
-
Description11(Z),14(Z),17(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid capable of maintaining continuous replication of functional mitochondria in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (KD115).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number17046-59-2
-
Formula Weight306.48
-
Molecular FormulaC20H34O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESC(CC/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\CC)CCCCCCC(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
all-trans-4-Oxoretin...
All-trans-4-Oxoretinoic acid is an active metabolite of vitamin A.
-
Angiotensinogen (1-1...
Angiotensinogen is a serum globulin formed by the liver that is cleaved by renin to form angiotensin I. Angiotensinogen is also called angiotensin precursor.
-
L-Lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It is a chiral molecule consisting of two optical isomers L-lactic acid and D-lactic acid with the L-isomer being the most common in living organisms. Lactic acid plays a role in several biochemical processes and is produced in the muscles during intense activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com

