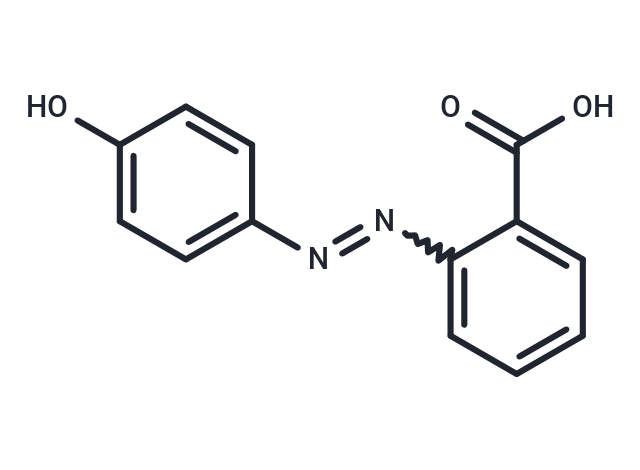
2-(4-Hydroxyphenylazo)benzoicacid
CAS No. 1634-82-8
2-(4-Hydroxyphenylazo)benzoicacid( —— )
Catalog No. M36947 CAS No. 1634-82-8
2-(4-Hydroxyphenylazo)benzoicacid is a spectrophotometric probe that shows changes in absorption spectra upon binding to proteins and binds to bovine serum proteins.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 34 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 47 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-(4-Hydroxyphenylazo)benzoicacid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2-(4-Hydroxyphenylazo)benzoicacid is a spectrophotometric probe that shows changes in absorption spectra upon binding to proteins and binds to bovine serum proteins.
-
Description2-(4-Hydroxyphenylazo)benzoicacid is a spectrophotometric probe that shows changes in absorption spectra upon binding to proteins and binds to bovine serum proteins.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1634-82-8
-
Formula Weight242.23
-
Molecular FormulaC13H10N2O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESOC(=O)c1ccccc1N=Nc1ccc(O)cc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
11-Oxomogroside IVa
The fruits of Siraitia grosvenorii Swingle.
-
Aminothiazole
Aminothiazole(2-Aminothiazole) is a beginning point for synthesis of many compounds including sulfur drugs, biocides, fungicides, dyes and chemical reaction accelerators.
-
3-Methoxymirificin
3'-Methoxymirificin is a natural product for research related to life sciences.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


