Pincainide
CAS No. 83471-41-4
Pincainide( —— )
Catalog No. M36382 CAS No. 83471-41-4
Pincainide is a novel beta-aminoaniline that inhibits, in a dose-dependent manner, diseases caused by abnormal norepinephrine vascular smooth muscle function.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 411 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 562 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 866 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePincainide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPincainide is a novel beta-aminoaniline that inhibits, in a dose-dependent manner, diseases caused by abnormal norepinephrine vascular smooth muscle function.
-
DescriptionPincainide is a novel beta-aminoaniline that inhibits, in a dose-dependent manner, diseases caused by abnormal norepinephrine vascular smooth muscle function.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number83471-41-4
-
Formula Weight260.37
-
Molecular FormulaC16H24N2O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
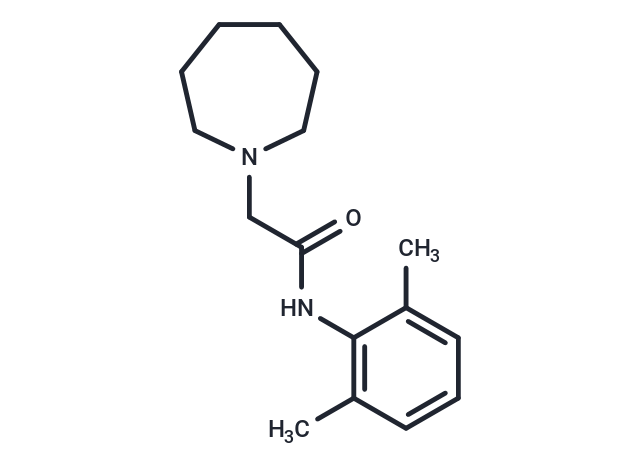
SMILESCC1=CC=CC(C)=C1NC(=O)CN1CCCCCC1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
WAY-659694
WAY-659694 shows moderate acute anti-inflammatory activity and analgesic activity in vivo.
-
(E)-SI-2
(E)-SI-2 is a potent small-molecule inhibitor of steroid receptor coactivator-3 (SRC-3 or AIB1) that can selectively inhibit the intrinsic transcriptional activities of SRC-3, also inhibits SRC-1 and SRC-2.
-
JHU-083
JHU-083, a proagent of 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine (DON), is an orally active and selective glutaminase antagonist. JHU-083 blocks glutaminase activity in brain CD11b+ cells and experimental cerebral malaria (ECM) resulting in a net decrease of glutamate levels in the animals.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


