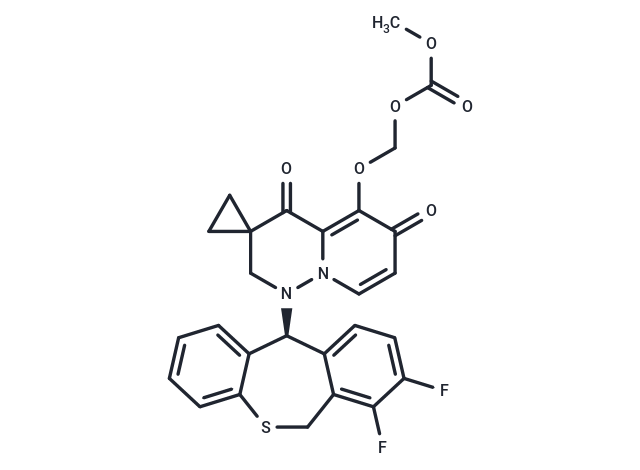
Cap-dependent endonuclease-IN-1
CAS No. 2365473-17-0
Cap-dependent endonuclease-IN-1( —— )
Catalog No. M35745 CAS No. 2365473-17-0
Cap-dependent endonuclease-IN-1 is a highly potent, orally active cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor with antiviral activity for studying influenza virus infection.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 1036 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 1568 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 2119 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 2585 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCap-dependent endonuclease-IN-1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCap-dependent endonuclease-IN-1 is a highly potent, orally active cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor with antiviral activity for studying influenza virus infection.
-
DescriptionCap-dependent endonuclease-IN-1 is an orally active cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor with high potency. Cap-dependent endonuclease-IN-1 can be used for the research of influenza.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2365473-17-0
-
Formula Weight540.54
-
Molecular FormulaC27H22F2N2O6S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C1C2(CN(N3C1=C(OCOC(OC)=O)C(=O)C=C3)[C@H]4C=5C(CSC=6C4=CC=CC6)=C(F)C(F)=CC5)CC2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Ming-Chu Hsu, et al. Cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitors. Patent WO2019144089A1.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Carasinol D
Carasinol D is a natural product from Carex humilis Leyss.
-
Yadanzigan
Yadanzigan (YDZG) is an anti-inflammatory agent and a NLRP3 inhibitor. Yadanzigan specifically inhibits NLRP3 activation via inhibiting NF-κB pathway and Reactive Oxygen Species production. Yadanzigan also moderates LPS -induced acute lung injury (ALI) in mice.
-
(S/R)-Orteronel
TAK-700 (Orteronel) is a potent and highly selective human 17, 20-lyase inhibitor with IC50 of 38 nM, exhibits >1000-fold selectivity over other CYPs (e.g. 11-hydroxylase and CYP3A4). Phase 3.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


