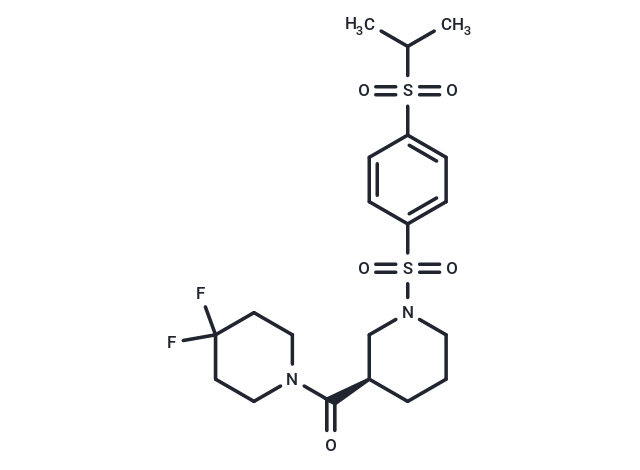
DX3-213B
CAS No. 2749555-66-4
DX3-213B( —— )
Catalog No. M35700 CAS No. 2749555-66-4
DX3-213B is a potent, orally active inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) complex I with an IC50 of 3.6 nM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 180 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 170 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 275 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 588 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 833 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1135 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDX3-213B
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDX3-213B is a potent, orally active inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) complex I with an IC50 of 3.6 nM.
-
DescriptionDX3-213B is a highly potent, orally active oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) complex I inhibitor (IC50=3.6 nM). DX3-213B impairs ATP generation (IC50=11 nM), and blocks MIA PaCa-2 cell growth (GI50=11 nM). DX3-213B is used for the research of the pancreatic cancer.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOXPHOS
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2749555-66-4
-
Formula Weight478.57
-
Molecular FormulaC20H28F2N2O5S2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 125 mg/mL (261.19 mM; Ultrasonic (<60°C)
-
SMILESCC(C)S(=O)(=O)c1ccc(cc1)S(=O)(=O)N1CCC[C@H](C1)C(=O)N1CCC(F)(F)CC1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Xue D, et al. Multiparameter Optimization of Oxidative Phosphorylation Inhibitors for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. J Med Chem. 2022;65(4):3404-3419. ?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Timosaponin A1
Timosaponin A1 is a coprostane type steroidal saponin isolated from Rhizoma Anemarrhenae.
-
Azimsulfuron
Azimsulfuron is a herbicide and can be used in the control of weeds in paddy fields.
-
1,1-Bis(Methylthio)-...
Bis(methylthio)-2-nitroethylene is an organic compound.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


