4-PQBH
CAS No. 2243355-51-1
4-PQBH( —— )
Catalog No. M35557 CAS No. 2243355-51-1
4-PQBH is a potent Nur77-binding agent with antitumour activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 105 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name4-PQBH
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description4-PQBH is a potent Nur77-binding agent with antitumour activity.
-
Description4-PQBH is a potent Nur77 binder (KD=1.17 μM). 4-PQBH extensively induces caspase-independent cytoplasmic vacuolization and paraptosis through Nur77-mediated ER stress and autophagy. 4-PQBH can be used for cancer research.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2243355-51-1
-
Formula Weight367.4
-
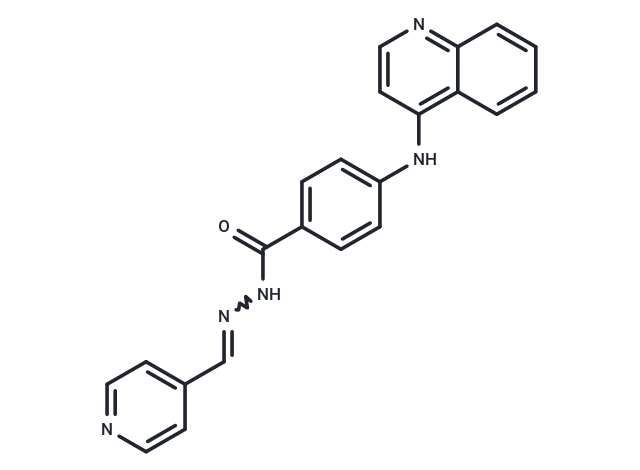
Molecular FormulaC22H17N5O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 25 mg/mL (68.05 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESO=C(NN=CC=1C=CN=CC1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)NC=3C=CN=C4C=CC=CC43
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Baicun Li, et al. Discovery of a Nur77-mediated cytoplasmic vacuolation and paraptosis inducer (4-PQBH) for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioorg Chem. 2022 Apr;121:105651.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
SAR7334 hydrochlorid...
SAR7334 hydrochloride, a potent and specific inhibitor of TRPC6 (IC50 of 7.9 nM), effectively targets and inhibits the TRPC6 channel.
-
Roemerine
Roemerine is a potential active xanthine oxidase(XOD) inhibitor, XOD is a key enzyme in the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia and also a well-known target for the drug development to treat gout.
-
Azosemide
Azosemide is a potent NKCC1 inhibitor (IC50s: 0.246?μM and 0.197?μM for hNKCC1A and NKCC1B).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


