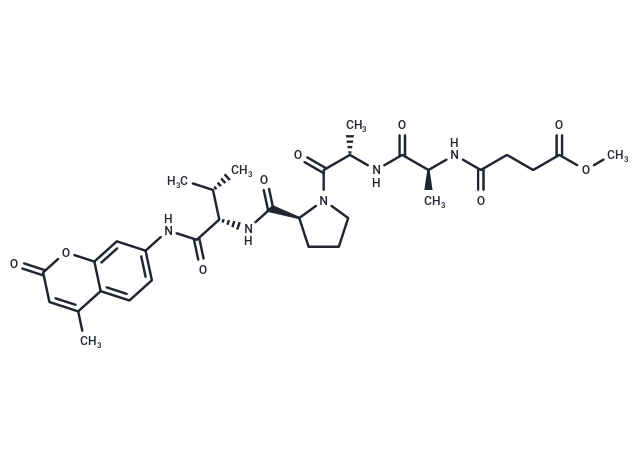
MeOSuc-AAPV-AMC
CAS No. 72252-90-5
MeOSuc-AAPV-AMC( —— )
Catalog No. M35029 CAS No. 72252-90-5
MeOSuc-AAPV-AMC (MeOSuc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Val-AMC) is a tetrapeptide that is a fluorescent substrate for human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 55 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 92 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 133 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 198 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMeOSuc-AAPV-AMC
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMeOSuc-AAPV-AMC (MeOSuc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Val-AMC) is a tetrapeptide that is a fluorescent substrate for human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase.
-
DescriptionMeOSuc-AAPV-AMC is a fluorogenic substrate for human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase (Km: 362 μM, Ex=380 nm, Em=460 nm).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number72252-90-5
-
Formula Weight627.69
-
Molecular FormulaC31H41N5O9
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 125 mg/mL (199.14 mM; Ultrasonic (<60°C)
-
SMILESCC=1C=2C(=CC(NC([C@@H](NC(=O)[C@H]3N(C([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC(CCC(OC)=O)=O)C)=O)C)=O)CCC3)[C@@H](C)C)=O)=CC2)OC(=O)C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Dmitri Ivanov, et al. A serpin from the gut bacterium Bifidobacterium longum inhibits eukaryotic elastase-like serine proteases. J Biol Chem. 2006 Jun 23;281(25):17246-17252. ?
molnova catalog



related products
-
2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4...
2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-Quinolone (Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal) is a quorum-sensing signalling molecule produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in response to increased cell density.
-
[Sar1, Ile8]-Angiote...
[Sar1, Ile8]-Angiotensin II (TFA) is a peptide that has multiple effects on vascular smooth muscle, including contraction of normal arteries and hypertrophy or hyperplasia of cultured cells or diseased vessels.
-
Trachelogenin
Trachelogenin, an HCV entry inhibitor, has antiproliferative effects, and its mechanism is related to affecting the phosphorylation of key proteins in the β-Catenin signaling pathway, such as β-Catenin, c-Myc, and GSK3, in a concentration-dependent manner.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


