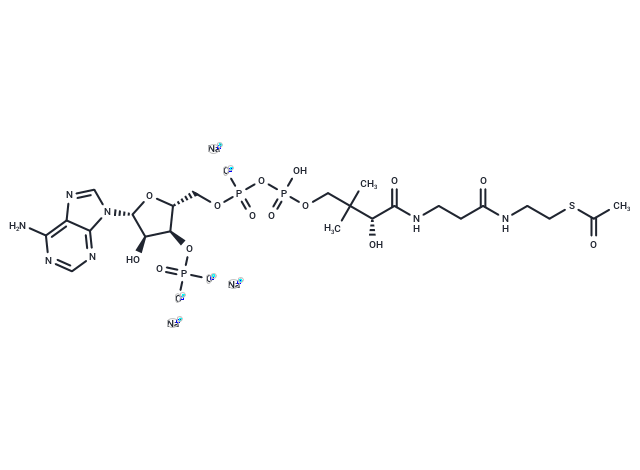
Acetyl Coenzyme A trisodium
CAS No. 102029-73-2
Acetyl Coenzyme A trisodium( —— )
Catalog No. M34989 CAS No. 102029-73-2
Acetyl Coenzyme A trisodium (Acetyl-CoA trisodium) is an important compound in glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism and is involved in the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 117 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAcetyl Coenzyme A trisodium
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAcetyl Coenzyme A trisodium (Acetyl-CoA trisodium) is an important compound in glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism and is involved in the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
-
DescriptionAcetyl-coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA) trisodium is a membrane-impermeant central metabolic intermediate, participates in the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation metabolism. Acetyl-coenzyme A trisodium, regulates various cellular mechanisms by providing (sole donor) acetyl groups to target amino acid residues for post-translational acetylation reactions of proteins. Acetyl Coenzyme A trisodium is also a key precursor of lipid synthesis.
-
In VitroAcetyl coenzyme A trisodium increases cytoplasmic protein acetylation in starved U2OS cells while reducing starvation-induced autophagic fluxes. (U2OS cells stably expressing GFP-LC3 and are microinjected with Acetyl coenzyme A trisodium; incubated in nutrient-free conditions in the presence of 100 nM BafA1 and fixed after 3 h).
-
In VivoAcetyl coenzyme A trisodium blunts pressure overload-induced cardiomyopathy in a mice cardiac pressure overload model by Suppressing maladaptive autophagy.Mice deprived of food (but with access to water ad libitum) for 24 h exhibit a significant reduction in total Acetyl coenzyme A trisodium levels in several organs, including the heart and muscles, corresponding to a decrease in protein acetylation levels. However, the same experimental conditions have no major effects on Acetyl coenzyme A trisodium concentrations in the brain and actually increase hepatic Acetyl coenzyme A trisodium and protein acetylation levels.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOXPHOS | Endogenous Metabolite | Autophagy
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number102029-73-2
-
Formula Weight875.52
-
Molecular FormulaC23H35N7Na3O17P3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 83.33 mg/mL (95.18 mM; Ultrasonic) DMSO : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble)
-
SMILESO[C@H]1[C@@H](O[C@@H]([C@H]1OP([O-])([O-])=O)COP(OP(OCC(C)(C)[C@@H](O)C(NCCC(NCCSC(C)=O)=O)=O)(O)=O)([O-])=O)N2C3=NC=NC(N)=C3N=C2.[Na+].[Na+].[Na+]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Choudhary C, et al. The growing landscape of lysine acetylation links metabolism and cell signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Aug;15(8):536-50. ?
molnova catalog



related products
-
5-Hydroxymethyldeoxy...
5-Hydroxymethyldeoxyuridine is an analog of nucleoside that has anticancer and antiviral activities.
-
23-Diaminopropionic ...
23-Diaminopropionic acid hydrochloride is a competitive inhibitor of cystathionase (CTH).
-
Didymin
Didymin has antioxidant property. Didymin induces apoptosis by inhibiting N-Myc and upregulating RKIP in neuroblastoma, may used for neuroblastoma therapy.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


