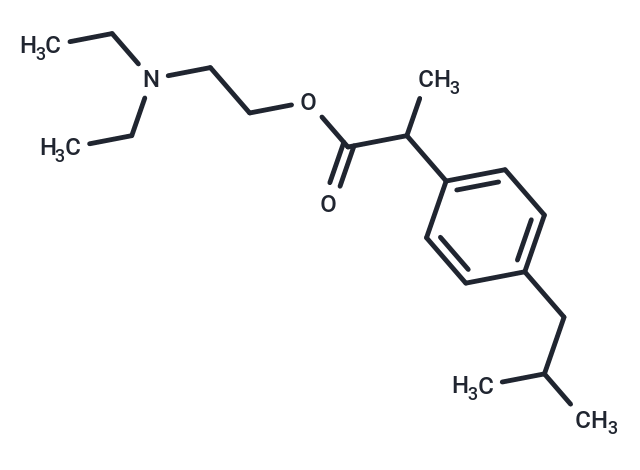
Ibuprofen diethylaminoethyl ester
CAS No. 64622-41-9
Ibuprofen diethylaminoethyl ester( —— )
Catalog No. M34279 CAS No. 64622-41-9
Ibuprofen diethylaminoethyl ester (BF DEAE) has anti-inflammatory activity, acts as a local anaesthetic and can be used in the study of neurological disorders.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 686 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 938 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 1444 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1841 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 2325 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameIbuprofen diethylaminoethyl ester
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionIbuprofen diethylaminoethyl ester (BF DEAE) has anti-inflammatory activity, acts as a local anaesthetic and can be used in the study of neurological disorders.
-
DescriptionIbuprofen diethylaminoethyl ester (BF DEAE) has anti-inflammatory activity, acts as a local anaesthetic and can be used in the study of neurological disorders.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number64622-41-9
-
Formula Weight305.45
-
Molecular FormulaC19H31NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C(OCCN(CC)CC)C(C1=CC=C(C=C1)CC(C)C)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
4-Borono-L-phenylala...
4-Borono-L-phenylalanine has antitumor activity and may be used in clinical trials of boron neutron capture therapy for the treatment of melanoma and glioblastoma multiforme.
-
NNC 63-0532
NOP receptor agonist.
-
N'-Methylnicotinamid...
N-methylnicotinamide is a metabolite of niacin (or nicotinamide) and is commonly found in human urine. However low levels of urinary excretion of N-methylnicotinamide indicates niacin deficiency. In patients with liver cirrhosis nicotinamide methylation is increased leading to a rise in urinary N-methylnicotinamide. N-methylnicotinamide has been found to be a microbial metabolite.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


