CCT077791
CAS No. 748777-47-1
CCT077791( —— )
Catalog No. M34060 CAS No. 748777-47-1
CCT077791 is a potent inhibitor of p300 and PCAF histone acetyltransferase activity for cancer research.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 1398 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1822 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 2250 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCCT077791
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCCT077791 is a potent inhibitor of p300 and PCAF histone acetyltransferase activity for cancer research.
-
DescriptionCCT077791 is a potent inhibitor of p300 and PCAF histone acetyltransferase activity for cancer research.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetEpigenetic Reader Domain
-
RecptorEpigenetic Reader Domain | Histone Acetyltransferase
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number748777-47-1
-
Formula Weight256.67
-
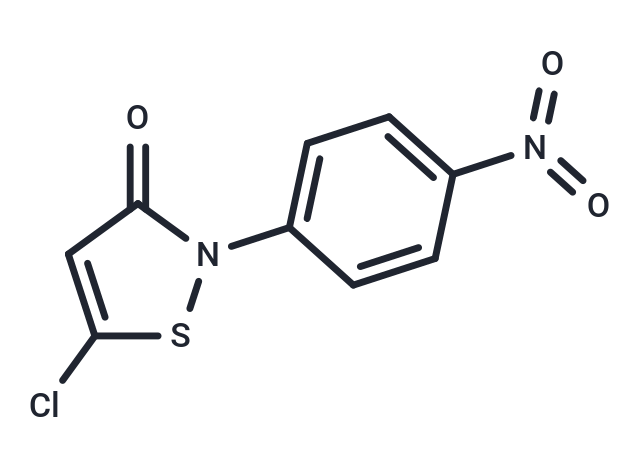
Molecular FormulaC9H5ClN2O3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C1N(SC(Cl)=C1)C2=CC=C(N(=O)=O)C=C2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
BRD4-BD1-IN-2
BRD4-BD1-IN-2 is a selective and potent BRD4-BD1 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 2.51 μM, exhibiting 20-fold greater inhibitory activity against BRD4-BD1 compared to BRD4-BD2.
-
TRIM24/BRPF1-IN-2
TRIM24/BRPF1-IN-2 is a selective dual TRIM24/BRPF1 inhibitor with anticancer activity that inhibits proliferation, gene and protein expression, and colony formation of prostate cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner.
-
ZEN-3411
ZEN-3411 is an orally available and potent BET inhibitor that inhibits BRD4(BD1), BRD4(BD2), and BRD4(BD1BD2) and suppresses the growth of tumor cells overproducing BET proteins.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


