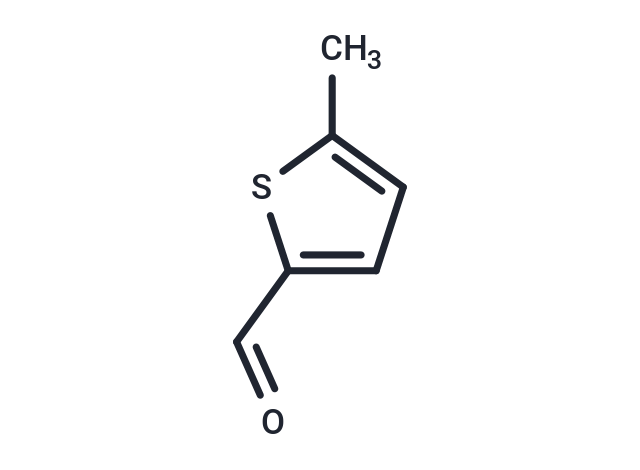
5-Methyl-2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde
CAS No. 13679-70-4
5-Methyl-2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde( —— )
Catalog No. M33587 CAS No. 13679-70-4
5-Methyl-2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde is a candidate microscopic third-order nonlinear optical (NLO) material.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 27 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name5-Methyl-2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description5-Methyl-2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde is a candidate microscopic third-order nonlinear optical (NLO) material.
-
Description5-Methyl-2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde actsas a candidate to microscopic third order non-linear optical (NLO) material.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number13679-70-4
-
Formula Weight126.18
-
Molecular FormulaC6H6OS
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (396.26 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESCc1ccc(C=O)s1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. DavutAvc?, et al. 5-Methyl-2-thiophenecarboxaldehyde: Experimental and TD/DFT study. Journal of Molecular Structure. 2018 Dec 15; 1174: 52-59.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Lushanrubescensin H
Lushanrubescensin H is a natural product from Isodon rubescens.
-
Mercurochrome
Mercurochrome
-
3-Acetylindole
3-Acetylindole can be used as a substituent and a probe to L-tryptophan for Sudlow site II.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


