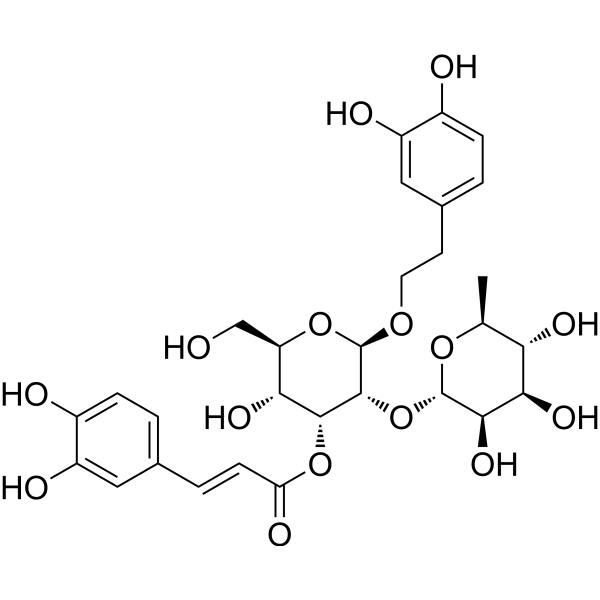
Magnoloside A
CAS No. 113557-95-2
Magnoloside A( —— )
Catalog No. M30848 CAS No. 113557-95-2
Magnoloside A has potent antifungal activities against various Cryptococcus strains with minimum inhibitory concentration values ranging from 1.0 to 4.0 ug/ml.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 295 | In Stock |


|
| 2MG | 113 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 190 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 280 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 472 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 672 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 918 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMagnoloside A
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMagnoloside A has potent antifungal activities against various Cryptococcus strains with minimum inhibitory concentration values ranging from 1.0 to 4.0 ug/ml.
-
DescriptionMagnoloside A has potent antifungal activities against various Cryptococcus strains with minimum inhibitory concentration values ranging from 1.0 to 4.0 ug/ml.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number113557-95-2
-
Formula Weight624.6
-
Molecular FormulaC29H36O15
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
2-Butylhexanoic acid
2-Butylhexanoic acid is an intermediate in organic synthesis.
-
11-Maleimidoundecano...
11-Maleimidoundecanoic acid is an alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
-
Imeglimin
Imeglimin (EMD 387008) is an orally available antidiabetic compound that enhances mitochondrial function, enhances insulin secretion, promotes β-cell proliferation and improves pancreatic β-cell survival in mice.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


