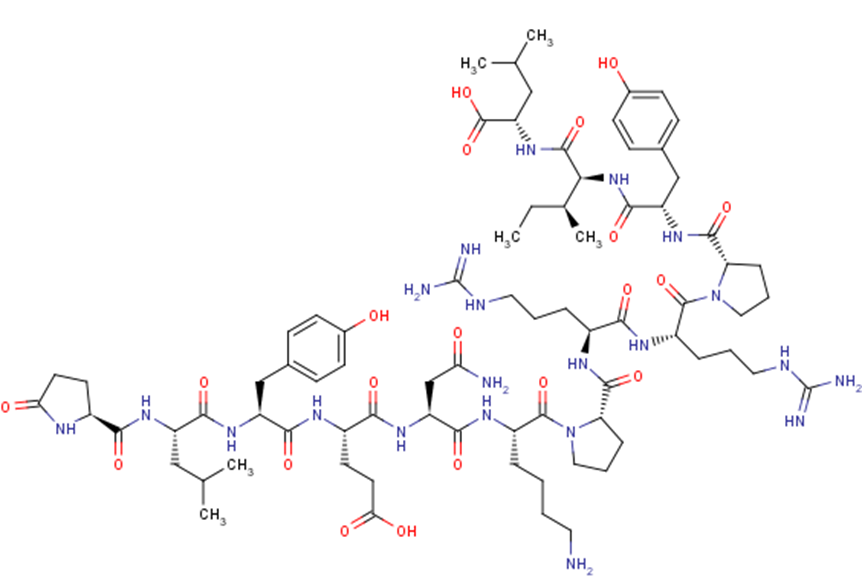
Neurotensin
CAS No. 39379-15-2
Neurotensin( —— )
Catalog No. M30009 CAS No. 39379-15-2
Neurotensin is a 13 amino acid neuropeptide that is implicated in the regulation of luteinizing hormone and prolactin release and has significant interaction with the dopaminergic system.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 76 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 154 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 217 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 435 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 613 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 860 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNeurotensin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNeurotensin is a 13 amino acid neuropeptide that is implicated in the regulation of luteinizing hormone and prolactin release and has significant interaction with the dopaminergic system.
-
DescriptionNeurotensin is a 13 amino acid neuropeptide that is implicated in the regulation of luteinizing hormone and prolactin release and has significant interaction with the dopaminergic system.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorNeurotensin receptors (NTR)
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number39379-15-2
-
Formula Weight1672.92
-
Molecular FormulaC78H121N21O20
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 33.33 mg/mL (19.92 mM)
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Fluoranthene
Fluoranthene is a chemical compound.
-
Lenthionine
Lenthionine is a marine derived natural products found in Chondria acrorhizophora.
-
MID-1
MID-1 is an inhibitor of MG53-IRS-1 (Mitsugumin 53-Insulin Receptor Substrate-1) interaction.?It disrupts molecular association of MG53 with IRS-1 and abolishes MG53-induced IRS-1 ubiquitination and degradation in skeletal muscle, leading to elevated IRS-1 expression level and increased insulin signaling and glucose uptake.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


