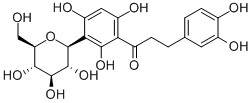
Aspalathin
CAS No. 6027-43-6
Aspalathin( —— )
Catalog No. M29643 CAS No. 6027-43-6
Aspalathin is a C-linked dihydrochalcone glucoside found in rooibos tea, a herbal tea prepared from the South African rooibos plant, Aspalathus linearis (Fabaceae).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAspalathin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAspalathin is a C-linked dihydrochalcone glucoside found in rooibos tea, a herbal tea prepared from the South African rooibos plant, Aspalathus linearis (Fabaceae).
-
DescriptionAspalathin is a C-linked dihydrochalcone glucoside found in rooibos tea, a herbal tea prepared from the South African rooibos plant, Aspalathus linearis (Fabaceae).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number6027-43-6
-
Formula Weight452.4
-
Molecular FormulaC21H24O11
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in methanol and water
-
SMILESC1=CC(=C(C=C1CCC(=O)C2=C(C(=C(C=C2O)O)C3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)O)O)O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
2F-Peracetyl-Fucose
2F-Peracetyl-Fucose (1,3,4-Tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-2-fluoro-L-fucopyranos) is a potent fucosyltransferase (FUT) inhibitor that suppresses salivary acidification and fucosylation in an in vitro inflammatory model.
-
Leuprolide Acetate
Leuprolide is an agonist at pituitary GnRH receptors. Leuprorelin is a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog used to treat a wide range of sex hormone-related disorders including advanced prostatic cancer endometriosis and precocious puberty.
-
1,16-Hexadecanediol
1,16-Hexadecanediol has low toxicity and can be used to make resins and nanomaterials.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


